Implications of vitamin D for flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): antioxidant ability, nutritional value, sensory quality, and myofiber characteristics
- PMID: 37759314
- PMCID: PMC10523690
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-023-00911-7
Implications of vitamin D for flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): antioxidant ability, nutritional value, sensory quality, and myofiber characteristics
Abstract
Background: Muscle represents a unique and complex system with many components and comprises the major edible part of animals. Vitamin D is a critical nutrient for animals and is known to enhance calcium absorption and immune response. In recent years, dietary vitamin D supplementation in livestock has received increased attention due to biological responses including improving shear force in mammalian meat. However, the vitamin D acquisition and myofiber development processes in fish differ from those in mammals, and the effect of vitamin D on fish flesh quality is poorly understood. Here, the influence of dietary vitamin D on fillet quality, antioxidant ability, and myofiber development was examined in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).
Methods: A total of 540 healthy grass carp, with an initial average body weight of 257.24 ± 0.63 g, were allotted in 6 experimental groups with 3 replicates each, and respectively fed corresponding diets with 15.2, 364.3, 782.5, 1,167.9, 1,573.8, and 1,980.1 IU/kg vitamin D for 70 d.
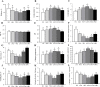
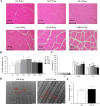
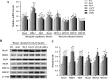
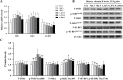
Results: Supplementation with 1,167.9 IU/kg vitamin D significantly improved nutritional value and sensory quality of fillets, enhancing crude protein, free amino acid, lipid, and collagen contents; maintaining an ideal pH; and reducing lactate content, shear force, and cooking loss relative to respective values in the control (15.2 IU/kg) group. Average myofiber diameter and the frequency of myofibers > 50 μm in diameter increased under supplementation with 782.5-1,167.9 IU/kg vitamin D. Levels of oxidative damage biomarkers decreased, and the expression of antioxidant enzymes and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling molecules was upregulated in the 1,167.9 IU/kg vitamin D treatment compared to respective values in the control group. Furthermore, vitamin D supplementation activated cell differentiation by enhancing the expression of myogenic regulatory factors and myocyte enhancer factors compared to that in the control group. In addition, supplementation with 1,167.9 IU/kg vitamin D improved protein deposition associated with protein synthesis molecule (target of rapamycin) signaling and vitamin D receptor paralogs, along with inhibition of protein degradation (forkhead box protein 1) signaling.
Conclusions: Overall, the results demonstrated that vitamin D strengthened antioxidant ability and myofiber development, thereby enhancing nutritional value and sensory quality of fish flesh. These findings suggest that dietary vitamin D supplementation is conducive to the production of nutrient-rich, high quality aquaculture products.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Grass carp; Myofiber development; Nutritional value; Sensory quality; Vitamin D.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures





References
-
- FAO. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in action. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organisation Of The United Nations; 2020. p. 9–65. 10.4060/ca9229en.
-
- Hosseini SV, Abedian KA, Rezaei M, Nazari RM, Feás X, Rabbani M. Influence of the in vivo addition of alpha-tocopheryl acetate with three lipid sources on the lipid oxidation and fatty acid composition of Beluga sturgeon, Huso huso, during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2010;118:341–48. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.131. - DOI
-
- Regost C, Arzel J, Cardinal M, Robin J, Laroche M, Kaushik SJ. Dietary lipid level, hepatic lipogenesis and flesh quality in turbot (Psetta maxima) Aquaculture. 2001;193:291–309. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00493-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

