The Impact of Ca2+ on Intracellular Distribution of Hemoglobin in Human Erythrocytes
- PMID: 37759502
- PMCID: PMC10526966
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12182280
The Impact of Ca2+ on Intracellular Distribution of Hemoglobin in Human Erythrocytes
Abstract
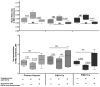
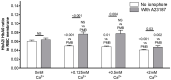
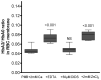
The membrane-bound hemoglobin (Hb) fraction impacts red blood cell (RBC) rheology and metabolism. Therefore, Hb-RBC membrane interactions are precisely controlled. For instance, the signaling function of membrane-bound deoxy-Hb and the structure of the docking sites in the cytosolic domain of the anion exchanger 1 (AE-1) protein are well documented; however, much less is known about the interaction of Hb variants with the erythrocyte's membrane. Here, we identified factors other than O2 availability that control Hb abundance in the membrane-bound fraction and the possible variant-specific binding selectivity of Hb to the membrane. We show that depletion of extracellular Ca2+ by chelators, or its omission from the extracellular medium, leads to membrane-bound Hb release into the cytosol. The removal of extracellular Ca2+ further triggers the redistribution of HbA0 and HbA2 variants between the membrane and the cytosol in favor of membrane-bound HbA2. Both effects are reversible and are no longer observed upon reintroduction of Ca2+ into the extracellular medium. Fluctuations of cytosolic Ca2+ also impact the pre-membrane Hb pool, resulting in the massive transfer of Hb to the cellular cytosol. We hypothesize that AE-1 is the specific membrane target and discuss the physiological outcomes and possible clinical implications of the Ca2+ regulation of the intracellular Hb distribution.
Keywords: calcium; hemoglobin A2; hemoglobin distribution; red blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Issaian A., Hay A., Dzieciatkowska M., Roberti D., Perrotta S., Darula Z., Redzic J., Busch M.P., Page G.P., Rogers S.C., et al. The Interactome of the N-Terminus of Band 3 Regulates Red Blood Cell Metabolism and Storage Quality. Haematologica. 2021;106:2971–2985. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.278252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

