Complement C3 Reduces Apoptosis via Interaction with the Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
- PMID: 37759504
- PMCID: PMC10528058
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12182282
Complement C3 Reduces Apoptosis via Interaction with the Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
Abstract
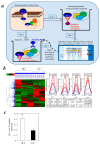
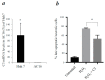
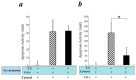
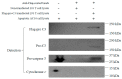
Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) elicits an acute inflammatory response involving complement factors. Recently, we reported that myocardial necrosis was decreased in complement C3-/- mice after heart I/R. The current study used the same heart model to test the effect of C3 on myocardial apoptosis and investigated if C3 regulation of apoptosis occurred in human cardiomyocytes. Comparative proteomics analyses found that cytochrome c was present in the myocardial C3 complex of WT mice following I/R. Incubation of exogenous human C3 reduced apoptosis in a cell culture system of human cardiomyocytes that did not inherently express C3. In addition, human C3 inhibited the intrinsic apoptosis pathway in a cell-free apoptosis system. Finally, human pro-C3 was found to bind with an apoptotic factor, pro-caspase 3, in a cell-free system. Thus, we present firsthand evidence showing that C3 readily reduces myocardial apoptosis via interaction with the intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis; complement C3; cytochrome c; ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI); pro-caspase 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

