Epidural Injection of Harpagoside for the Recovery of Rats with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- PMID: 37759506
- PMCID: PMC10526993
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12182281
Epidural Injection of Harpagoside for the Recovery of Rats with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Abstract
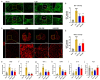
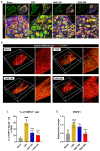
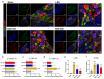
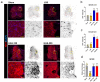
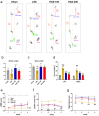
Epidural administration is the leading therapeutic option for the management of pain associated with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS), which is characterized by compression of the nerve root due to narrowing of the spinal canal. Corticosteroids are effective in alleviating LSS-related pain but can lead to complications with long-term use. Recent studies have focused on identifying promising medications administered epidurally to affected spinal regions. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effectiveness of harpagoside (HAS) as an epidural medication in rats with LSS. HAS at various concentrations was effective for neuroprotection against ferrous sulfate damage and consequent promotion of axonal outgrowth in primary spinal cord neurons. When two concentrations of HAS (100 and 200 μg/kg) were administered to the rat LSS model via the epidural space once a day for 4 weeks, the inflammatory responses around the silicone block used for LSS were substantially reduced. Consistently, pain-related factors were significantly suppressed by the epidural administration of HAS. The motor functions of rats with LSS significantly improved. These findings suggest that targeted delivery of HAS directly to the affected area via epidural injection holds promise as a potential treatment option for the recovery of patients with LSS.
Keywords: epidural injection; harpagoside; inflammation; lumbar spinal stenosis; neuropathic pain; pain relief.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

