New Propargyloxy Derivatives of Galangin, Kaempferol and Fisetin-Synthesis, Spectroscopic Analysis and In Vitro Anticancer Activity on Head and Neck Cancer Cells
- PMID: 37759511
- PMCID: PMC10528839
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12182288
New Propargyloxy Derivatives of Galangin, Kaempferol and Fisetin-Synthesis, Spectroscopic Analysis and In Vitro Anticancer Activity on Head and Neck Cancer Cells
Abstract
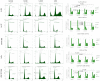
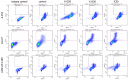
Head and neck cancer (HNC) therapy is limited; therefore, new solutions are increasingly being sought among flavonoids, which exhibit numerous biological properties, including potential anticancer activity. However, because they are mostly insoluble in water, are unstable and have low bioavailability, they are subjected to chemical modification to obtain new derivatives with better properties. This study aimed to synthesize and analyze new propargyloxy derivatives of galangin, kaempferol and fisetin, and to evaluate their anticancer activity against selected HNC cell lines. The obtained derivatives were assessed by spectroscopic analysis; next, their anticancer activity was evaluated using a flow cytometer and real-time cell analysis. The results showed that only the fisetin derivative was suitable for further analysis, due to the lack of crystal formation of the compound. The fisetin derivative statistically significantly increases the number of cells in the G2/M phase (p < 0.05) and increases cyclin B1 levels. A statistically significant increase in the number of apoptotic cells after being exposed to the tested compound was also observed (p < 0.05). The data indicate that the obtained fisetin derivative exhibits anticancer activity by affecting the cell cycle and increasing apoptosis in selected HNC lines, which suggests its potential use as a new medicinal agent in the future.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; cyclin; flavonol; flow cytometry; head and neck cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kaempferol and Fisetin-Related Signaling Pathways Induce Apoptosis in Head and Neck Cancer Cells.Cells. 2023 Jun 6;12(12):1568. doi: 10.3390/cells12121568. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371038 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Potential of Selected Flavonols: Fisetin, Kaempferol, and Quercetin on Head and Neck Cancers.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 5;13(3):845. doi: 10.3390/nu13030845. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33807530 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer activity of Fisetin against the human osteosarcoma cell lines involves G2/M cell cycle arrest, mitochondrial apoptosis and inhibition of cell migration and invasion.J BUON. 2020 Mar-Apr;25(2):1022-1027. J BUON. 2020. Retraction in: J BUON. 2021 Mar-Apr;26(2):641. PMID: 32521901 Retracted.
-
Physico-chemical and Biological Evaluation of Flavonols: Fisetin, Quercetin and Kaempferol Alone and Incorporated in beta Cyclodextrins.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(4):615-626. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160621105306. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27338298
-
Fisetin, a Potent Anticancer Flavonol Exhibiting Cytotoxic Activity against Neoplastic Malignant Cells and Cancerous Conditions: A Scoping, Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 23;14(13):2604. doi: 10.3390/nu14132604. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807785 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, Pharmacological Properties, and Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Antitumor Activity of Betulin and Its Derivatives in Gastrointestinal Cancers.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 13;15(12):2768. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122768. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dynamics simulation-driven focused virtual screening and experimental validation of Fisetin as an inhibitor of Helicobacter pylori HtrA protease.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb 23. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11137-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39988708
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

