TRPV1 Channels Are New Players in the Reticulum-Mitochondria Ca2+ Coupling in a Rat Cardiomyoblast Cell Line
- PMID: 37759544
- PMCID: PMC10529771
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12182322
TRPV1 Channels Are New Players in the Reticulum-Mitochondria Ca2+ Coupling in a Rat Cardiomyoblast Cell Line
Abstract
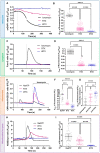
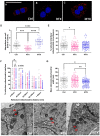
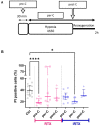
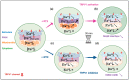
The Ca2+ release in microdomains formed by intercompartmental contacts, such as mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs), encodes a signal that contributes to Ca2+ homeostasis and cell fate control. However, the composition and function of MAMs remain to be fully defined. Here, we focused on the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a Ca2+-permeable ion channel and a polymodal nociceptor. We found TRPV1 channels in the reticular membrane, including some at MAMs, in a rat cardiomyoblast cell line (SV40-transformed H9c2) by Western blotting, immunostaining, cell fractionation, and proximity ligation assay. We used chemical and genetic probes to perform Ca2+ imaging in four cellular compartments: the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), cytoplasm, mitochondrial matrix, and mitochondrial surface. Our results showed that the ER Ca2+ released through TRPV1 channels is detected at the mitochondrial outer membrane and transferred to the mitochondria. Finally, we observed that prolonged TRPV1 modulation for 30 min alters the intracellular Ca2+ equilibrium and influences the MAM structure or the hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death. Thus, our study provides the first evidence that TRPV1 channels contribute to MAM Ca2+ exchanges.
Keywords: Ca2+ homeostasis; ER–mitochondria contact sites; H9c2; TRP channels; TRPV1; hypoxia–reoxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the study’s design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

