Recent Advances in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: From Nirmatrelvir to Future Perspectives
- PMID: 37759739
- PMCID: PMC10647625
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13091339
Recent Advances in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: From Nirmatrelvir to Future Perspectives
Abstract
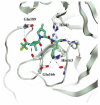
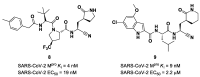
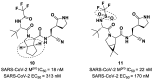
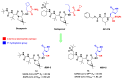
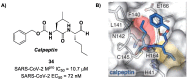
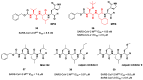
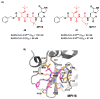
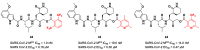
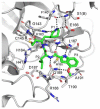
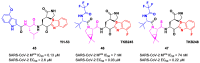
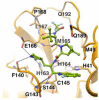
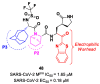
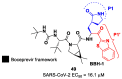
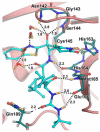
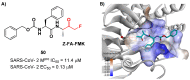
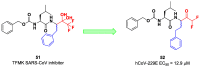
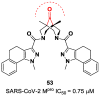
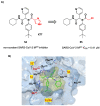
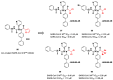
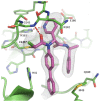
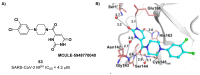
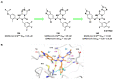
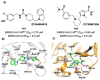
The main protease (Mpro) plays a pivotal role in the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and is considered a highly conserved viral target. Disruption of the catalytic activity of Mpro produces a detrimental effect on the course of the infection, making this target one of the most attractive for the treatment of COVID-19. The current success of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor Nirmatrelvir, the first oral drug for the treatment of severe forms of COVID-19, has further focused the attention of researchers on this important viral target, making the search for new Mpro inhibitors a thriving and exciting field for the development of antiviral drugs active against SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses.
Keywords: COVID-19; Paxlovid; SARS-CoV-2 Mpro; coronavirus; nirmatrelvir; peptidomimetics; protease inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





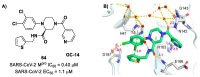


Similar articles
-
Silaproline-bearing nirmatrelvir derivatives are potent inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease highlighting the value of silicon-derivatives in structure-activity-relationship studies.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Jul 5;291:117603. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117603. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40220677
-
Exploring epigenetic drugs as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: a docking and MD simulation study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(13):6892-6903. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2236714. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37458994
-
AI-driven covalent drug design strategies targeting main protease (mpro) against SARS-CoV-2: structural insights and molecular mechanisms.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025 Jul;43(11):5436-5464. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2308769. Epub 2024 Jan 29. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025. PMID: 38287509 Review.
-
Genetic Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Reveals High Sequence and Structural Conservation Prior to the Introduction of Protease Inhibitor Paxlovid.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0086922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00869-22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35862764 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Approach for the Identification of Natural Products Active against SARS-CoV-2.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 28;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/biom14010043. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38254643 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring TMPRSS2 Drug Target to Combat Influenza and Coronavirus Infection.Scientifica (Cairo). 2025 Apr 21;2025:3687892. doi: 10.1155/sci5/3687892. eCollection 2025. Scientifica (Cairo). 2025. PMID: 40297833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning-Guided Screening and Molecular Docking for Proposing Naturally Derived Drug Candidates Against MERS-CoV 3CL Protease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 26;26(7):3047. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073047. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243651 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Predictors of Paxlovid Treatment Response: The Role of IFNAR2, OAS1, OAS3, and ACE2 in COVID-19 Clinical Course.J Pers Med. 2025 Apr 17;15(4):156. doi: 10.3390/jpm15040156. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40278335 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Viral and Cellular Cysteine Proteases for Treatment of New Variants of SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2024 Feb 22;16(3):338. doi: 10.3390/v16030338. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543704 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

