Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: Recent Advancements
- PMID: 37759787
- PMCID: PMC10527030
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13091387
Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: Recent Advancements
Abstract
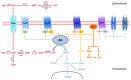
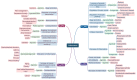
Adenosine receptors (ARs) are widely acknowledged pharmacological targets yet are still underutilized in clinical practice. Their ubiquitous distribution in almost all cells and tissues of the body makes them, on the one hand, excellent candidates for numerous diseases, and on the other hand, intrinsically challenging to exploit selectively and in a site-specific manner. This review endeavors to comprehensively depict the substantial advancements witnessed in recent years concerning the development of drugs that modulate ARs. Through preclinical and clinical research, it has become evident that the modulation of ARs holds promise for the treatment of numerous diseases, including central nervous system disorders, cardiovascular and metabolic conditions, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, and cancer. The latest studies discussed herein shed light on novel mechanisms through which ARs exert control over pathophysiological states. They also introduce new ligands and innovative strategies for receptor activation, presenting compelling evidence of efficacy along with the implicated signaling pathways. Collectively, these emerging insights underscore a promising trajectory toward harnessing the therapeutic potential of these multifaceted targets.
Keywords: A1; A2A; A2B; A3; adenosine; adenosine receptors; therapeutic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

