Impact of Polyphenols on Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Factors in Diabetes Mellitus: Nutritional Antioxidants and Their Application in Improving Antidiabetic Therapy
- PMID: 37759802
- PMCID: PMC10526737
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13091402
Impact of Polyphenols on Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Factors in Diabetes Mellitus: Nutritional Antioxidants and Their Application in Improving Antidiabetic Therapy
Abstract
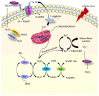
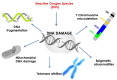
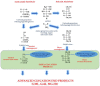
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress. Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the development and progression of diabetes and its complications. Nutritional antioxidants derived from dietary sources have gained significant attention due to their potential to improve antidiabetic therapy. This review will delve into the world of polyphenols, investigating their origins in plants, metabolism in the human body, and relevance to the antioxidant mechanism in the context of improving antidiabetic therapy by attenuating oxidative stress, improving insulin sensitivity, and preserving β-cell function. The potential mechanisms of, clinical evidence for, and future perspectives on nutritional antioxidants as adjuvant therapy in diabetes management are discussed.
Keywords: diabetes; inflammation; oxidative stress; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the links between polyphenols, Nrf2, and diabetes: A review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 May;186:118020. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118020. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40168723 Review.
-
Food Polyphenols and Type II Diabetes Mellitus: Pharmacology and Mechanisms.Molecules. 2023 May 10;28(10):3996. doi: 10.3390/molecules28103996. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Diabetic, and Pro-Osteogenic Activities of Polyphenols for the Treatment of Two Different Chronic Diseases: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoporosis.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 11;14(7):836. doi: 10.3390/biom14070836. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Rich-Polyphenols Extract of Dendrobium loddigesii on Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidant, and Gut Microbiota Modulation in db/db Mice.Molecules. 2018 Dec 7;23(12):3245. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123245. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30544624 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic and Renoprotective Effects of Coffea arabica Pulp Aqueous Extract through Preserving Organic Cation Transport System Mediated Oxidative Stress Pathway in Experimental Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Molecules. 2021 Mar 28;26(7):1907. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071907. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33800673 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glucose Metabolism-Modifying Natural Materials for Potential Feed Additive Development.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 13;16(9):1208. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091208. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Bioactive Compounds in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 6;26(3):1379. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031379. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Citrus Species Against Metabolic Syndrome: Insights from Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Curr Nutr Rep. 2025 Aug 13;14(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s13668-025-00691-8. Curr Nutr Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804580 Review.
-
Integrated in vitro, in silico, and in vivo approaches to elucidate the antidiabetic mechanisms of Cicer arietinum and Hordeum vulgare extract and secondary metabolites.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;15(1):6620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89642-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39994296 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of dietary total antioxidant capacity to type 2 diabetes risk and levels of glycemic biomarkers: a systematic review.Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2025 Apr;16(2):100-115. doi: 10.24171/j.phrp.2024.0337. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40139760 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

