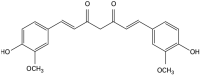
Curcumin as a Potential Antioxidant in Stress Regulation of Terrestrial, Avian, and Aquatic Animals: A Review
- PMID: 37760003
- PMCID: PMC10525612
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12091700
Curcumin as a Potential Antioxidant in Stress Regulation of Terrestrial, Avian, and Aquatic Animals: A Review
Abstract
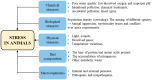
Stress has brought about a variety of harmful impacts on different animals, leading to difficulties in the management of animal husbandry and aquaculture. Curcumin has been recognized as a potential component to ameliorate the adverse influence of animal stress induced by toxicity, inflammation, diseases, thermal effect, and so on. In detail, this compound is known to offer various outstanding functions, including antibacterial properties, antioxidant effects, immune response recovery, and behavioral restoration of animals under stress conditions. However, curcumin still has some limitations, owing to its low bioavailability. This review summarizes the latest updates on the regulatory effects of curcumin in terms of stress management in terrestrial, avian, and aquatic animals.
Keywords: antioxidants; aquatic animals; avian; curcumin; stress management; terrestrial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the review article was written in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential protective roles of curcumin against cadmium-induced toxicity and oxidative stress.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2021 Apr 3;24(3):95-118. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2020.1860842. Epub 2020 Dec 23. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2021. PMID: 33357071 Review.
-
Curcumin-Loaded Nanocapsules Reverses the Depressant-Like Behavior and Oxidative Stress Induced by β-Amyloid in Mice.Neuroscience. 2019 Dec 15;423:122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.09.032. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 31698022
-
Curcumin loaded chitosan nanoparticles fortify shrimp feed pellets with enhanced antioxidant activity.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Jan;120:111737. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111737. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 33545880
-
Different Curcumin-Loaded Delivery Systems for Wound Healing Applications: A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 22;15(1):38. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010038. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant effects of curcumin in models of neurodegeneration, aging, oxidative and nitrosative stress: A review.Neuroscience. 2019 May 15;406:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.02.020. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30825584 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin enhances ATG3-dependent autophagy and inhibits metastasis in cervical carcinoma.Cell Div. 2024 Nov 28;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00138-6. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 39609925 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Induced Liver Injury Associated with Turmeric and Piperine: A Case and Review.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2025 Feb 24;19(1):96-106. doi: 10.1159/000543679. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39995754 Free PMC article.
-
The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of reactive oxygen species in the malignant transformation of viral hepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma: a new insight.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jun 14;30(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00745-3. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40517270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the mechanisms behind the hepatoprotective properties of curcumin.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Aug;98(8):2331-2351. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03758-7. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38837048 Review.
-
Trials for reducing the dangerous effect on poultry fed on aflatoxin contaminated ration using nano curcumin.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Feb 17;21(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04519-z. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 39962519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee H.B., Yoon J.H., Park J.Y., Lee I.Y., Lim H.K. A comparison of the physiological responses to heat stress of juvenile and adult starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus) Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh. 2021;73:1–15. doi: 10.46989/001c.31303. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources