Selenium-Fortified Kombucha-Pollen Beverage by In Situ Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles with High Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 37760014
- PMCID: PMC10525527
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12091711
Selenium-Fortified Kombucha-Pollen Beverage by In Situ Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles with High Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
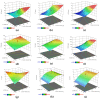
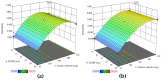
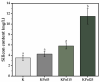
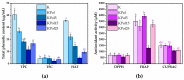
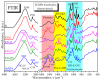
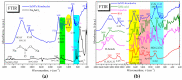
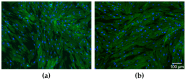
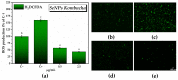
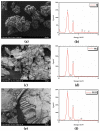
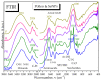
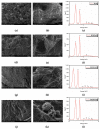
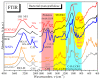
Biogenic selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) have been shown to exhibit increased bioavailability. Fermentation of pollen by a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeasts (SCOBY/Kombucha) leads to the release of pollen content and enhances the prebiotic and probiotic effects of Kombucha. The aim of this study was to fortify Kombucha beverage with SeNPs formed in situ by Kombucha fermentation with pollen. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was used to optimize the biosynthesis of SeNPs and the pollen-fermented Kombucha beverage. SeNPs were characterized by Transmission electron microscopy energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (TEM-EDX), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Dynamic light scattering (DLS), and Zeta potential. The pollen-fermented Kombucha beverage enriched with SeNPs was characterized by measuring the total phenolic content, antioxidant activity, soluble silicon, saccharides, lactic acid, and the total content of Se0. The polyphenols were identified by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). The pollen and the bacterial (nano)cellulose were characterized by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), FTIR, and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). We also assessed the in vitro biocompatibility in terms of gingival fibroblast viability and proliferation, as well as the antioxidant activity of SeNPs and the pollen-fermented Kombucha beverage enriched with SeNPs. The results highlight their increased biological performance in this regard.
Keywords: antioxidant; biocompatible; biogenic nanoselenium; kombucha fermentation; response surface methodology; selenium-nanoparticles-enriched bee bread.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Cytocompatibility, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of a Mucoadhesive Biopolymeric Hydrogel Embedding Selenium Nanoparticles Phytosynthesized by Sea Buckthorn Leaf Extract.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;17(1):23. doi: 10.3390/ph17010023. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256857 Free PMC article.
-
Bee Collected Pollen with Enhanced Health Benefits, Produced by Fermentation with a Kombucha Consortium.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 23;10(10):1365. doi: 10.3390/nu10101365. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30249054 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides and proteins-capped selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393.Carbohydr Polym. 2018 Sep 1;195:576-585. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.110. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Carbohydr Polym. 2018. PMID: 29805014
-
Kombucha Tea-A Double Power of Bioactive Compounds from Tea and Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeasts (SCOBY).Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;10(10):1541. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101541. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidisciplinary advances in kombucha fermentation, health efficacy, and market evolution.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Aug 5;206(9):366. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04086-1. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39098983 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytocompatibility, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of a Mucoadhesive Biopolymeric Hydrogel Embedding Selenium Nanoparticles Phytosynthesized by Sea Buckthorn Leaf Extract.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;17(1):23. doi: 10.3390/ph17010023. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256857 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Hydrogel Formulation Based on Ferulic Acid-Grafted Nano-Chitosan and Bacterial Nanocellulose Enriched with Selenium Nanoparticles from Kombucha Fermentation.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jul 22;15(7):202. doi: 10.3390/jfb15070202. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39057323 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Alginate Oligosaccharides Attenuate Heat Stress-Induced Impairment of Breast Meat Quality via Regulating Oxidative Stress, Metabolome and Ferroptosis in Broilers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;12(12):2032. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122032. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136152 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Kombucha Fermentation on Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Monofloral Rapeseed Bee-Collected Pollen.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 18;14(6):752. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060752. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563384 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Properties and Sensory Quality of Kombucha Analogs Based on Herbal Infusions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;13(10):1191. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101191. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aylanc V., Larbi S., Calhelha R., Barros L., Rezouga F., Rodríguez-Flores M.S., Seijo M.C., El Ghouizi A., Lyoussi B., Falcão S.I., et al. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Anticancer Activity of Mono- and Polyfloral Moroccan Bee Pollen by Characterizing Phenolic and Volatile Compounds. Molecules. 2023;28:835. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020835. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uțoiu E., Matei F., Toma A., Diguță C.F., Ștefan L.M., Mănoiu S., Vrăjmașu V.V., Moraru I., Oancea A., Israel-Roming F., et al. Bee Collected Pollen with Enhanced Health Benefits, Produced by Fermentation with a Kombucha Consortium. Nutrients. 2018;10:1365. doi: 10.3390/nu10101365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352-SECVENT, Sequential processes to close bioeconomy side stream and innovative bioproducts resulted from these, contract 81/2016, SMIS 105684, subsidiary projects 1393/2022 FructiRan/Cohesion funds of the European Union
- 366/PED/Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CNCS/CCCDI - UEFISCDI, PNCDI III
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

