Antifungal Action of Arabidopsis thaliana TCP21 via Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis
- PMID: 37760070
- PMCID: PMC10525234
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12091767
Antifungal Action of Arabidopsis thaliana TCP21 via Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis
Abstract
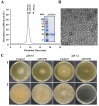
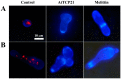
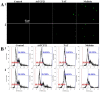
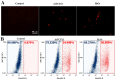
The realm of antimicrobial proteins in plants is extensive but remains relatively uncharted. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the action of plant antifungal proteins (AFPs) holds promise for antifungal strategies. This study aimed to bridge this knowledge gap by comprehensively screening Arabidopsis thaliana species to identify novel AFPs. Using MALDI-TOF analysis, we identified a member of the TEOSINTE BRANCHED1/CYCLOIDEA/PROLIFERATING CELL FACTOR1 (TCP) family of transcription factors as a novel AFP, A. thaliana TCP21 (AtTCP21; accession number NP_196450). Bacterially purified recombinant AtTCP21 inhibited the growth of various pathogenic fungal cells. AtTCP21 was more potent than melittin, a well-known AFP, in combating Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Growth inhibition assays against various fungal pathogens and yeasts confirmed the pH-dependent antimicrobial activity of AtTCP21. Without inducing any membrane alterations, AtTCP21 penetrates the fungal cell wall and membrane, where it instigates a repressive milieu for fungal cell growth by generating intracellular reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial superoxides; resulting in morphological changes and apoptosis. Our findings demonstrate the redox-regulating effects of AtTCP21 and point to its potential as an antimicrobial agent.
Keywords: TCP; antifungal protein; apoptosis; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


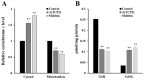
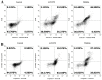
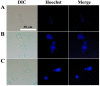

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

