Bioprocessing Considerations towards the Manufacturing of Therapeutic Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 37760170
- PMCID: PMC10525286
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10091067
Bioprocessing Considerations towards the Manufacturing of Therapeutic Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
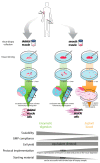
Tissue engineering approaches within the muscle context represent a promising emerging field to address the current therapeutic challenges related with multiple pathological conditions affecting the muscle compartments, either skeletal muscle or smooth muscle, responsible for involuntary and voluntary contraction, respectively. In this review, several features and parameters involved in the bioprocessing of muscle cells are addressed. The cell isolation process is depicted, depending on the type of tissue (smooth or skeletal muscle), followed by the description of the challenges involving the use of adult donor tissue and the strategies to overcome the hurdles of reaching relevant cell numbers towards a clinical application. Specifically, the use of stem/progenitor cells is highlighted as a source for smooth and skeletal muscle cells towards the development of a cellular product able to maintain the target cell's identity and functionality. Moreover, taking into account the need for a robust and cost-effective bioprocess for cell manufacturing, the combination of muscle cells with biomaterials and the need for scale-up envisioning clinical applications are also approached.
Keywords: cell manufacturing; skeletal muscle cells; smooth muscle cells; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adult stem cell sources for skeletal and smooth muscle tissue engineering.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Apr 11;13(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02835-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35410452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Converging functionality: Strategies for 3D hybrid-construct biofabrication and the role of composite biomaterials for skeletal regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2021 Sep 15;132:188-216. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33713862 Review.
-
Addressing the Manufacturing Challenges of Cell-Based Therapies.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2020;171:225-278. doi: 10.1007/10_2019_118. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31844924
-
Biomaterials based strategies for skeletal muscle tissue engineering: existing technologies and future trends.Biomaterials. 2015;53:502-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.110. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25890747 Review.
-
Enhanced elastin synthesis and maturation in human vascular smooth muscle tissue derived from induced-pluripotent stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 1;52:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.083. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28163239
Cited by
-
Xenogeneic-free platform for the isolation and scalable expansion of human bladder smooth muscle cells.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025 Feb 11;46:e00878. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2025.e00878. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40094098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dumont N.A., Bentzinger C.F., Sincennes M., Rudnicki M.A. Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Compr. Physiol. 2015;5:1027–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

