Abnormal Fetal Lung of Hoxa1-/- Piglets Is Rescued by Maternal Feeding with All-Trans Retinoic Acid
- PMID: 37760250
- PMCID: PMC10525738
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13182850
Abnormal Fetal Lung of Hoxa1-/- Piglets Is Rescued by Maternal Feeding with All-Trans Retinoic Acid
Abstract
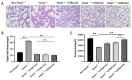
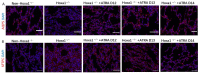
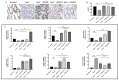
Neonatal Hoxa1-/- piglets were characterized by dyspnea owing to the Hoxa1 mutation, and maternal administration with ATRA alleviated the dyspnea of neonatal Hoxa1-/- piglets. The purpose of this experiment was to explore how maternal ATRA administration rescued the abnormal fetal lungs of Hoxa1-/- piglets. Samples of the lungs were collected from neonatal Hoxa1-/- and non-Hoxa1-/- piglets delivered by sows in the control group, and from neonatal Hoxa1-/- piglets born by sows administered with ATRA at 4 mg/kg body weight on dpc 12, 13, or 14, respectively. These were used for the analysis of ELISA, histological morphology, immunofluorescence staining, immunohistochemistry staining, and quantitative real-time PCR. The results indicate that the Hoxa1 mutation had adverse impacts on the development of the alveoli and pulmonary microvessels of Hoxa1-/- piglets. Maternal administration with ATRA at 4 mg/kg body weight on dpc 14 rescued the abnormal lung development of Hoxa1-/- piglets by increasing the IFN-γ concentration (p < 0.05), airspace area (p < 0.01) and pulmonary microvessel density (p < 0.01); increasing the expression of VEGFD (p < 0.01), PDGFD (p < 0.01), KDR (p < 0.01), ID1 (p < 0.01), and NEDD4 (p < 0.01); and decreasing the septal wall thickness (p < 0.01) and the expression of SFTPC (p < 0.01) and FOXO3 (p < 0.01). Maternal administration with ATRA plays a vital role in rescuing the abnormal development of lung of Hoxa1-/- fetal piglets.
Keywords: ATRA; Hoxa1 mutation; alveoli; fetal piglets; maternal administration; pulmonary blood vessel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Administration of All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Pregnant Sows Improves the Developmental Defects of Hoxa1-/- Fetal Pigs.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jan 11;7:618660. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.618660. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33506002 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Pregnant Sows Alters Gut Bacterial Community of Neonatal Piglets With Different Hoxa1 Genotypes.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 26;12:712212. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.712212. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34381436 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of all-trans retinoic acid upregulates leptin signaling in hypoplastic rat lungs with experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia.Pediatr Surg Int. 2014 Dec;30(12):1183-90. doi: 10.1007/s00383-014-3605-8. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Pediatr Surg Int. 2014. PMID: 25330951
-
Prenatal retinoic acid increases lipofibroblast expression in hypoplastic rat lungs with experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia.J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jun;49(6):876-81; discussion 881. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.01.017. Epub 2014 Feb 3. J Pediatr Surg. 2014. PMID: 24888826
-
Role of Maternal Dietary Protein and Amino Acids on Fetal Programming, Early Neonatal Development, and Lactation in Swine.Animals (Basel). 2019 Jan 13;9(1):19. doi: 10.3390/ani9010019. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30642135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Homeobox A1 in Airway Epithelial Generation from Human Airway Basal Cells.Cells. 2025 Apr 5;14(7):549. doi: 10.3390/cells14070549. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214503 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

