PorcineAI-Enhancer: Prediction of Pig Enhancer Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
- PMID: 37760334
- PMCID: PMC10526013
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13182935
PorcineAI-Enhancer: Prediction of Pig Enhancer Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
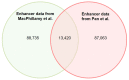
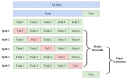
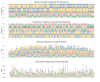
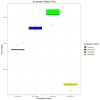
Understanding the mechanisms of gene expression regulation is crucial in animal breeding. Cis-regulatory DNA sequences, such as enhancers, play a key role in regulating gene expression. Identifying enhancers is challenging, despite the use of experimental techniques and computational methods. Enhancer prediction in the pig genome is particularly significant due to the costliness of high-throughput experimental techniques. The study constructed a high-quality database of pig enhancers by integrating information from multiple sources. A deep learning prediction framework called PorcineAI-enhancer was developed for the prediction of pig enhancers. This framework employs convolutional neural networks for feature extraction and classification. PorcineAI-enhancer showed excellent performance in predicting pig enhancers, validated on an independent test dataset. The model demonstrated reliable prediction capability for unknown enhancer sequences and performed remarkably well on tissue-specific enhancer sequences.The study developed a deep learning prediction framework, PorcineAI-enhancer, for predicting pig enhancers. The model demonstrated significant predictive performance and potential for tissue-specific enhancers. This research provides valuable resources for future studies on gene expression regulation in pigs.
Keywords: convolutional neural networks; enhancer; sequence classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beagan J.A., Pastuzyn E.D., Fernandez L.R., Guo M.H., Feng K., Titus K.R., Chandrashekar H., Shepherd J.D., Phillips-Cremins J.E. Three-dimensional genome restructuring across timescales of activity-induced neuronal gene expression. Nat. Neurosci. 2020;23:707–717. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0634-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

