Chinese Herbal Extracts Mitigate Ammonia Generation in the Cecum of Laying Hens: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 37760368
- PMCID: PMC10525658
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13182969
Chinese Herbal Extracts Mitigate Ammonia Generation in the Cecum of Laying Hens: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
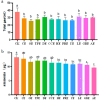
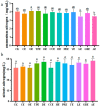
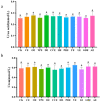
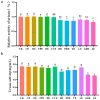
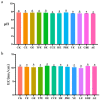
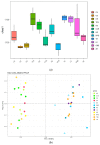
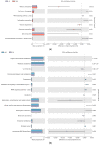
The objectives of the study were to screen one or several Chinese herbal extracts with good ammonia emission reduction effects using an in vitro gas production study. The study consisted of a control (without Chinese herbal extract), and 11 experimental groups with added cinnamon extract (CE), Osmanthus extract (OE), tangerine peel extract (TPE), dandelion extract (DE), Coptis chinensis extract (CCE), honeysuckle extract (HE), Pulsatilla root extract (PRE), yucca extract (YE), licorice extract (LE), Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE), or astragalus extract (AE). The results showed that HE, PRE, YE, LE, GBE, and AE significantly reduced ammonia production (p ≤ 0.05). The most significant ammonia inhibition was achieved via AE, resulting in a 26.76% reduction. In all treatments, Chinese herbal extracts had no significant effect on pH, conductivity, or uric acid, urea, and nitrate-nitrogen concentrations (p > 0.05). However, AE significantly reduced urease activity and the relative activity of uricase (p ≤ 0.05). AE significantly increased the relative abundance of Bacteroides and decreased the relative abundance of Clostridium, Desulfovibrio, and Prevotell (p ≤ 0.05). Astragalus extract inhibited ammonia emission from laying hens by changing the gut microbial community structure, reducing the relative abundance of ammonia-producing bacteria, and reducing microorganisms' uricase and urease activities.
Keywords: Chinese herbal extract; ammonia; astragalus extract; gut microbiota; laying hen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shah S.W.A., Chen J., Han Q., Xu Y., Ishfaq M., Teng X. Ammonia Inhalation Impaired Immune Function and Mitochondrial Integrity in the Broilers Bursa of Fabricius: Implication of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020;190:110078. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110078. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Swelum A.A., El-Saadony M.T., Abd El-Hack M.E., Abo Ghanima M.M., Shukry M., Alhotan R.A., Hussein E.O.S., Suliman G.M., Ba-Awadh H., Ammari A.A., et al. Ammonia Emissions in Poultry Houses and Microbial Nitrification as a Promising Reduction Strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;781:146978. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146978. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 31972610/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022KJ128/The Construction Project of Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance in Guangdong Province
- 2023KJ128/The Construction Project of Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance in Guangdong Province
- YUECAINONG202137/The Guangdong agricultural research projects
- DT20220020/The Heyuan Branch, Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

