The Prognostic Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in Stage IIIC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 37760482
- PMCID: PMC10526430
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15184512
The Prognostic Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in Stage IIIC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
Background: We sought to determine the prognostic value of the newly developed Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in patients with stage IIIC non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who underwent definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT).
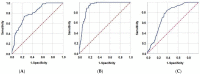
Methods: This study was conducted on a cohort of 802 newly diagnosed stage IIIC NSCLC patients who underwent CCRT. The novel GINI created first here was defined as follows: GINI = [C-reactive protein × Platelets × Monocytes × Neutrophils] ÷ [Albumin × Lymphocytes]. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the optimal pre-CCRT GINI cut-off value that substantially interacts with the locoregional progression-free (LRPFS), progression-free (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results: The optimal pre-CCRT GINI cutoff was 1562 (AUC: 76.1%; sensitivity: 72.4%; specificity: 68.2%; Youden index: 0.406). Patients presenting with a GINI ≥ 1562 had substantially shorter median LRPFS (13.3 vs. 18.4 months; p < 0.001), PFS (10.2 vs. 14.3 months; p < 0.001), and OS (19.1 vs. 37.8 months; p < 0.001) durations than those with a GINI < 1562. Results of the multivariate analysis revealed that the pre-CCRT GINI ≥ 1562 (vs. <1562), T4 tumor (vs. T3), and receiving only 1 cycle of concurrent chemotherapy (vs. 2-3 cycles) were the factors independently associated with poorer LRPS (p < 0.05 for each), PFS (p < 0.05 for each), and OS (p < 0.05 for each).
Conclusion: The newly developed GINI index efficiently divided the stage IIIC NSCLSC patients into two subgroups with substantially different median and long-term survival outcomes.
Keywords: Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index; biological marker; chemoradiotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index as a novel comprehensive biomarker in predicting the radiation-induced trismus rates in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Oct 17;24(6):1703-1710. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10616. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38860864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The global immune-nutrition-inflammation index (GINI) as a robust prognostic factor in glioblastoma patients treated with the standard stupp protocol.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241284089. doi: 10.1177/03946320241284089. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39305006 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Novel CARWL Score in Stage IIIC Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy.Can Respir J. 2024 Jun 28;2024:2803044. doi: 10.1155/2024/2803044. eCollection 2024. Can Respir J. 2024. PMID: 38975012 Free PMC article.
-
High pre-chemoradiotherapy pan-immune-inflammation value levels predict worse outcomes in patients with stage IIIB/C non-small-cell lung cancer.Discov Oncol. 2023 Dec 13;14(1):230. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00851-8. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38091179 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of overall concurrent chemoradiotherapy duration on survival outcomes of stage IIIB/C non-small-cell lung carcinoma patients: Analysis of 956 patients.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 22;14(7):e0218627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218627. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31329602 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Predictive Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) on Survival Outcomes in Patients with Grade 4 Adult-Type Diffuse Gliomas.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 28;31(9):5027-5039. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31090372. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39330000 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram based on the advanced lung cancer inflammation index and other relevant clinical factors for patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14465-6. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597903 Free PMC article.
-
Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index as a novel comprehensive biomarker in predicting the radiation-induced trismus rates in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Oct 17;24(6):1703-1710. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10616. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38860864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional status of patients with driver gene mutation-negative non-small cell lung cancer after postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jun 30;17(6):4189-4197. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-822. Epub 2025 Jun 17. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688293 Free PMC article.
-
The global immune-nutrition-inflammation index (GINI) as a robust prognostic factor in glioblastoma patients treated with the standard stupp protocol.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241284089. doi: 10.1177/03946320241284089. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39305006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gray J.E., Villegas A., Daniel D., Vicente D., Murakami S., Hui R., Kurata T., Chiappori A., Lee K.H., Cho B.C., et al. Three-Year Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC—Update from PACIFIC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020;15:288–293. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.10.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Topkan E., Selek U., Kucuk A., Haksoyler V., Ozdemir Y., Sezen D., Mertsoylu H., Besen A.A., Bolukbasi Y., Ozyilkan O., et al. Prechemoradiotherapy Systemic inflammation response index stratifies stage iiib/c non-small-cell lung cancer pa-tients into three prognostic groups: A propensity score-matching analysis. J. Oncol. 2021;2021:6688138. doi: 10.1155/2021/6688138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oberije C., De Ruysscher D., Houben R., van de Heuvel M., Uyterlinde W., Deasy J.O., Belderbos J., Dingemans A.-M.C., Rimner A., Din S., et al. A Validated Prediction Model for Overall Survival From Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Toward Survival Prediction for Individual Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015;92:935–944. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.02.048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

