The Prognostic Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in Stage IIIC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 37760482
- PMCID: PMC10526430
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15184512
The Prognostic Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in Stage IIIC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
Background: We sought to determine the prognostic value of the newly developed Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) in patients with stage IIIC non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who underwent definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT).
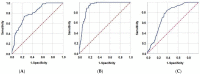
Methods: This study was conducted on a cohort of 802 newly diagnosed stage IIIC NSCLC patients who underwent CCRT. The novel GINI created first here was defined as follows: GINI = [C-reactive protein × Platelets × Monocytes × Neutrophils] ÷ [Albumin × Lymphocytes]. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the optimal pre-CCRT GINI cut-off value that substantially interacts with the locoregional progression-free (LRPFS), progression-free (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results: The optimal pre-CCRT GINI cutoff was 1562 (AUC: 76.1%; sensitivity: 72.4%; specificity: 68.2%; Youden index: 0.406). Patients presenting with a GINI ≥ 1562 had substantially shorter median LRPFS (13.3 vs. 18.4 months; p < 0.001), PFS (10.2 vs. 14.3 months; p < 0.001), and OS (19.1 vs. 37.8 months; p < 0.001) durations than those with a GINI < 1562. Results of the multivariate analysis revealed that the pre-CCRT GINI ≥ 1562 (vs. <1562), T4 tumor (vs. T3), and receiving only 1 cycle of concurrent chemotherapy (vs. 2-3 cycles) were the factors independently associated with poorer LRPS (p < 0.05 for each), PFS (p < 0.05 for each), and OS (p < 0.05 for each).
Conclusion: The newly developed GINI index efficiently divided the stage IIIC NSCLSC patients into two subgroups with substantially different median and long-term survival outcomes.
Keywords: Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index; biological marker; chemoradiotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gray J.E., Villegas A., Daniel D., Vicente D., Murakami S., Hui R., Kurata T., Chiappori A., Lee K.H., Cho B.C., et al. Three-Year Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC—Update from PACIFIC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020;15:288–293. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.10.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Topkan E., Selek U., Kucuk A., Haksoyler V., Ozdemir Y., Sezen D., Mertsoylu H., Besen A.A., Bolukbasi Y., Ozyilkan O., et al. Prechemoradiotherapy Systemic inflammation response index stratifies stage iiib/c non-small-cell lung cancer pa-tients into three prognostic groups: A propensity score-matching analysis. J. Oncol. 2021;2021:6688138. doi: 10.1155/2021/6688138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oberije C., De Ruysscher D., Houben R., van de Heuvel M., Uyterlinde W., Deasy J.O., Belderbos J., Dingemans A.-M.C., Rimner A., Din S., et al. A Validated Prediction Model for Overall Survival From Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Toward Survival Prediction for Individual Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015;92:935–944. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.02.048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

