Prognostic Value of Necroptosis-Related Genes Signature in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 37760507
- PMCID: PMC10527362
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15184539
Prognostic Value of Necroptosis-Related Genes Signature in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
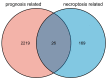
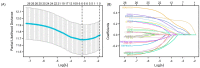
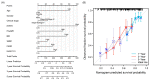
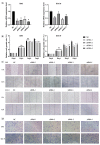
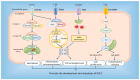
The dual role of necroptosis in inhibiting and promoting tumor development has gradually received much attention because of its essential significance for targeted treatment. Accordingly, this study aims to explore the relationship between necroptosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), and search for novel prognostic factors for OSCC. RNA-seq data and clinical information were downloaded from TCGA and GTEx databases. The prognostic signature of necroptosis-related genes (NRGs) was constructed by univariate Cox regression analysis and the LASSO Cox regression model. Moreover, survival analyses, ROC curves, and nomograms were adopted to further analyze. GO and KEGG analyses and immune infiltration analyses were used for function enrichment and immune feature research in turn. The NRG prognostic signature expression was higher in OSCC tissues than in normal tissues, and the overall survival (OS) rate of the high-expression group was much lower. HPRT1 was proved to be an independent prognostic factor in OSCC. Furthermore, the function enrichment analyses revealed that NRGs were involved in necroptosis, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune reaction. The expression of NRGs was related to immunosuppression in OSCC. Furthermore, the knockdown of HPRT1 could suppress the proliferation and migration of OSCC. In conclusion, the high expression of NRG prognostic signature is associated with poor prognosis in OSCC, and HPRT1 can serve as a novel independent prognostic factor for OSCC.
Keywords: HPRT1; biomarker; necroptosis; oral squamous cell carcinoma; prognostic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Narrative Review of Prognostic Gene Signatures in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using LASSO Cox Regression.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 8;13(1):134. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010134. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a necroptosis-related prognostic gene signature associated with tumor immune microenvironment in cervical carcinoma and experimental verification.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Oct 17;20(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02802-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36253777 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of necroptosis-related prognostic gene signature and tumor immune microenvironment infiltration characterization in esophageal carcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul 15;22(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02423-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35840882 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic signature based on necroptosis-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 16;18(2):e0279744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279744. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36795724 Free PMC article.
-
A novel necroptosis-related gene index for predicting prognosis and a cold tumor immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:968165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968165. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Cisplatin promotes TNF-α autocrine to trigger RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Oct 20;44(10):1947-1954. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39523095 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Apoptosis, Autophagic Cell Death, Necroptosis, Pyroptosis, and Ferroptosis Pathways in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Strategies.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 16;13(7):1745. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071745. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring beyond Common Cell Death Pathways in Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;13(2):103. doi: 10.3390/biology13020103. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Prognostic Gene Signatures in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using LASSO Cox Regression.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 8;13(1):134. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010134. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

