A TLR4 Agonist Induces Osteosarcoma Regression by Inducing an Antitumor Immune Response and Reprogramming M2 Macrophages to M1 Macrophages
- PMID: 37760603
- PMCID: PMC10526955
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15184635
A TLR4 Agonist Induces Osteosarcoma Regression by Inducing an Antitumor Immune Response and Reprogramming M2 Macrophages to M1 Macrophages
Abstract
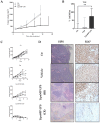
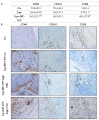
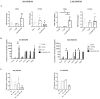
Osteosarcoma (OsA) has limited treatment options and stagnant 5-year survival rates. Its immune microenvironment is characterized by a predominance of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), whose role in OsA progression remain unclear. Nevertheless, immunotherapies aiming to modulate macrophages activation and polarization could be of interest for OsA treatment. In this study, the antitumor effect of a liposome-encapsulated chemically detoxified lipopolysaccharide (Lipo-MP-LPS) was evaluated as a therapeutic approach for OsA. Lipo-MP-LPS is a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist sufficiently safe and soluble to be IV administered at effective doses. Lipo-MP-LPS exhibited a significant antitumor response, with tumor regression in 50% of treated animals and delayed tumor progression in the remaining 50%. The agent inhibited tumor growth by 75%, surpassing the efficacy of other immunotherapies tested in OsA. Lipo-MP-LPS modulated OsA's immune microenvironment by favoring the transition of M2 macrophages to M1 phenotype, creating a proinflammatory milieu and facilitating T-cell recruitment and antitumor immune response. Overall, the study demonstrates the potent antitumor effect of Lipo-MP-LPS as monotherapy in an OsA immunocompetent model. Reprogramming macrophages and altering the immune microenvironment likely contribute to the observed tumor control. These findings support the concept of immunomodulatory approaches for the treatment of highly resistant tumors like OsA.
Keywords: growth inhibition; immunotherapy TLR4 agonist; macrophages reprograming; osteosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A detoxified TLR4 agonist inhibits tumour growth and lung metastasis of osteosarcoma by promoting CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocyte infiltration.BJC Rep. 2025 Jan 27;3(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s44276-024-00120-3. BJC Rep. 2025. PMID: 39870886 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel Reduces Tumor Growth by Reprogramming Tumor-Associated Macrophages to an M1 Profile in a TLR4-Dependent Manner.Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 15;78(20):5891-5900. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3480. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30104241
-
A systemically administered detoxified TLR4 agonist displays potent antitumor activity and an acceptable tolerance profile in preclinical models.Front Immunol. 2023 May 8;14:1066402. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1066402. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37223101 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming Induces Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 7;13:840029. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840029. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages with Anticancer Therapies: Radiotherapy versus Chemo- and Immunotherapies.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 14;8:828. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00828. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28769933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scutellarein Inhibits Osteosarcoma Growth by Targeting the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 6;19:51-64. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S489092. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39803606 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of M1 Macrophages and Their Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2024 Aug 26;13(17):1428. doi: 10.3390/cells13171428. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of research hotspots and evolutionary trends in osteosarcoma pulmonary metastasis: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis spanning five decades.J Orthop. 2025 Apr 5;63:181-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2025.03.053. eCollection 2025 May. J Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40291605
-
Advancements in osteosarcoma management: integrating immune microenvironment insights with immunotherapeutic strategies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 10;12:1394339. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1394339. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38915446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microenvironment matters: insights from the FOSTER consortium on microenvironment-driven approaches to osteosarcoma therapy.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025 Apr 10;44(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s10555-025-10257-3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025. PMID: 40210800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smeland S., Bielack S.S., Whelan J., Bernstein M., Hogendoorn P., Krailo M.D., Gorlick R., Janeway K.A., Ingleby F.C., Anninga J., et al. Survival and Prognosis with Osteosarcoma: Outcomes in More than 2000 Patients in the EURAMOS-1 (European and American Osteosarcoma Study) Cohort. Eur. J. Cancer. 2019;109:36–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.11.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perry J.A., Kiezun A., Tonzi P., Van Allen E.M., Carter S.L., Baca S.C., Cowley G.S., Bhatt A.S., Rheinbay E., Pedamallu C.S., et al. Complementary Genomic Approaches Highlight the PI3K/MTOR Pathway as a Common Vulnerability in Osteosarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E5564–E5573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419260111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

