Virtual Screening of Potential RoxS Inhibitors and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Activity in Combination with Antibiotics against Clinically Resistant Bacteria
- PMID: 37760718
- PMCID: PMC10525716
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12091422
Virtual Screening of Potential RoxS Inhibitors and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Activity in Combination with Antibiotics against Clinically Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
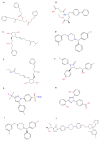
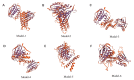
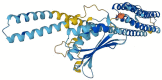
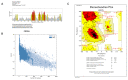
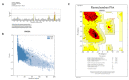
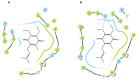
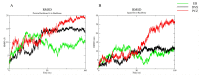
Pseudomonas aeruginosa with difficult-to-treat resistance has been designated as an urgent or serious threat by the CDC in the United States; therefore, novel antibacterial drugs and combination strategies are urgently needed. The sensor kinase RoxS is necessary for the aerobic growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This study aimed to screen candidate RoxS inhibitors and evaluate their efficacy in treating multi-drug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in combination with meropenem and amikacin to identify promising combination strategies. RoxS protein structures were constructed using homology modeling and potential RoxS inhibitors, including Ezetimibe, Deferasirox, and Posaconazole, were screened from the FDA-approved ZINC drug database using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. MIC and checkerboard assays were used to determine the in vitro antimicrobial efficacy of the three drugs in combination with antibiotics. The results of in vitro experiments showed an additive effect of 100 μg/mL Deferasirox or 16 μg/mL Posaconazole in combination with meropenem and a synergistic effect of 1.5 μg/mL Deferasirox and amikacin. In summary, these three drugs are potential inhibitors of RoxS, and their combination with meropenem or amikacin is expected to reverse the resistance of P. aeruginosa, providing new combination strategies for the treatment of clinically difficult-to-treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; RoxS; checkerboard assay; homology modeling; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Time-Kill Evaluation of Antibiotic Combinations Containing Ceftazidime-Avibactam against Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Their Potential Role against Ceftazidime-Avibactam-Resistant Isolates.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0058521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00585-21. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34319141 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of two antimicrobial peptides, Nisin and P10 with conventional antibiotics against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates.Microb Pathog. 2021 Jan;150:104700. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104700. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33346078
-
Colistin plus meropenem combination is synergistic in vitro against extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including high-risk clones.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2019 Sep;18:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 May 30. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2019. PMID: 31154007
-
[Antimicrobial activity of carbapenems and the combined effect with aminoglycoside against recent clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa].Jpn J Antibiot. 2002 Apr;55(2):181-6. Jpn J Antibiot. 2002. PMID: 12071095 Japanese.
-
Effect of Imipenem and Amikacin Combination against Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;10(11):1429. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111429. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahramian A., Khoshnood S., Shariati A., Doustdar F., Chirani A.S., Heidary M. Molecular characterization of the pilS2 gene and its association with the frequency of Pseudomonas aeruginosa plasmid pKLC102 and PAPI-1 pathogenicity island. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019;12:221–227. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S188527. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

