Comprehensive Analysis Identifies PKP3 Overexpression in Pancreatic Cancer Related to Unfavorable Prognosis
- PMID: 37760912
- PMCID: PMC10526039
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11092472
Comprehensive Analysis Identifies PKP3 Overexpression in Pancreatic Cancer Related to Unfavorable Prognosis
Abstract
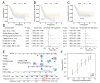
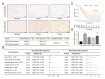
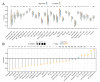
Plakophilin 3 (PKP3) affects cell signal transduction and cell adhesion and performs a crucial function in tumorigenesis. The current investigation evaluated the predictive significance and underlying processes of PKP3 within pancreatic cancer (PC) tissues. The assessment of differences in PKP3 expression was conducted through an analysis of RNA-seq data acquired from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. Additionally, clinical samples were collected to validate the findings. The predictive significance of PKP3 was investigated by analyzing survival data derived from TCGA and clinical specimens. PKP3's biological function was assessed via phenotypic experiments after the suppression of PKP3 expression within PC cells. Functional enrichment analysis, encompassing KEGG, GO, and GSEA, was employed to assess the underlying mechanism of PKP3. Immune infiltration analysis was conducted in the present investigation to determine the association between PKP3 and tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TICs). In PC tissues, PKP3 expression was abnormally upregulated and correlated with a negative prognosis in individuals with PC. PKP3 can promote the progression, migration, and invasive capacity of PC cells and is relevant to the regulation of the PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Immune infiltration analysis demonstrated that PKP3 impeded CD8+ T-cell infiltration and immune cytokine expression within the tumor microenvironment. The PKP3 protein was identified as a prospective independent predictive indicator and represents a viable approach for immunotherapy in the context of PC. PKP3 may impact prognosis by broadly inhibiting immune cell infiltration and promoting the activation of tumor-associated signaling pathways.
Keywords: PKP3; biomarker; immune infiltration; pancreatic cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immunocyte Infiltration Analysis and Immunohistochemistry Identify EVL as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer.J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 28;13(3):433. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030433. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36983615 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of LIPH as an unfavorable biomarkers correlated with immune suppression or evasion in pancreatic cancer based on RNA-seq.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Mar;71(3):601-612. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03019-x. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 34279685 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine-modified circIGF2BP3 inhibits CD8+ T-cell responses to facilitate tumor immune evasion by promoting the deubiquitination of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cancer. 2021 Aug 20;20(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01398-4. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34416901 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of role of GPRASP1, associated with clinical outcomes, immune microenvironment, and immunotherapeutic efficiency in pancreatic cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Mar;243:154374. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154374. Epub 2023 Feb 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36801507
-
Identify potential prognostic indicators and tumor-infiltrating immune cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2022 Feb 25;42(2):BSR20212523. doi: 10.1042/BSR20212523. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35083488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of necroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by miR‑10b‑5p through modulation of the PKP3/RIPK3/MLKL cascade.Oncol Rep. 2025 May;53(5):56. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8889. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40116080 Free PMC article.
-
KRT6A, KRT6B, PKP1, and PKP3 as key hub genes in esophageal cancer: A combined bioinformatics and experimental study.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jun 22;43:102095. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102095. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40612005 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Tools That Identify Tumor Cells by Inferring Copy Number Variations from Single-Cell Experiments in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 5;12(8):1759. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081759. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grossberg A.J., Chu L.C., Deig C.R., Fishman E.K., Hwang W.L., Maitra A., Marks D.L., Mehta A., Nabavizadeh N., Simeone D.M., et al. Multidisciplinary standards of care and recent progress in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70:375–403. doi: 10.3322/caac.21626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 82260555/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- lzuyxcx-2022-177/Medical Innovation and Development Project of Lanzhou University
- 22ZD6FA021-4/Major Science and Technology Projects of Gansu Province
- No. 2020-ZD-60/Lanzhou Science and Technology Plan Project
- No. ZYZX-2020-08/Open Project of Gansu Provincial Key Laboratory for Mining and Innovation Transformation of Traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

