Communicator Extraordinaire: Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment Are Essential Local and Long-Distance Mediators of Cancer Metastasis
- PMID: 37760975
- PMCID: PMC10526527
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11092534
Communicator Extraordinaire: Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment Are Essential Local and Long-Distance Mediators of Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
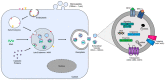
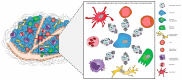
Human tumors are increasingly being described as a complex "ecosystem", that includes many different cell types, secreted growth factors, extracellular matrix (ECM) components, and microvessels, that altogether create the tumor microenvironment (TME). Within the TME, epithelial cancer cells control the function of surrounding stromal cells and the non-cellular ECM components in an intricate orchestra of signaling networks specifically designed for cancer cells to exploit surrounding cells for their own benefit. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) released into the tumor microenvironment are essential mediators in the reprogramming of surrounding stromal cells, which include cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and tumor endothelial cells (TECs), which are responsible for the promotion of neo-angiogenesis, immune cell evasion, and invasion which are essential for cancer progression. Perhaps most importantly, tumor-derived EVs play critical roles in the metastatic dissemination of tumor cells through their two-fold role in initiating cancer cell invasion and the establishment of the pre-metastatic niche, both of which are vital for tumor cell migration, homing, and colonization at secondary tumor sites. This review discusses extracellular vesicle trafficking within the tumor microenvironment and pre-metastatic niche formation, focusing on the complex role that EVs play in orchestrating cancer-to-stromal cell communication in order to promote the metastatic dissemination of cancer cells.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer; cell-to-cell communication; extracellular vesicles; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unlocking the Secrets of Extracellular Vesicles: Orchestrating Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics in Metastasis, Drug Resistance, and Immune Evasion.J Cancer. 2024 Oct 14;15(19):6383-6415. doi: 10.7150/jca.98426. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39513123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts creates a pre-metastatic niche in the lung through activating fibroblasts.Mol Cancer. 2019 Dec 3;18(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1101-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31796058 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2016 Dec 12;30(6):836-848. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.009. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 27960084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma-derived extracellular vesicles instigate proinflammatory signaling in the metastatic microenvironment.Int J Cancer. 2019 Nov 1;145(9):2521-2534. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32521. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31216364
-
Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles and Cellular Communication in Metastasis.Cells. 2021 Dec 6;10(12):3429. doi: 10.3390/cells10123429. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of immunotherapy in targeting tumor microenvironment in genitourinary cancers.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1506278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1506278. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40260236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive detection of orthotopic human lung tumors by microRNA expression profiling of mouse exhaled breath condensates and exhaled extracellular vesicles.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024;5(1):138-164. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.77. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024. PMID: 38863869 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Exosomes in Cancer and Aptamer-Modified Exosomes as a Promising Platform for Cancer Targeted Therapy.Biol Proced Online. 2024 May 27;26(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12575-024-00245-2. Biol Proced Online. 2024. PMID: 38802766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-derived vesicles in immune modulation: focus on signaling pathways.Front Immunol. 2025 May 15;16:1581964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1581964. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40443670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment Modulation by Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2024 Apr 15;13(8):682. doi: 10.3390/cells13080682. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

