MicroRNA-21 Silencing in Diabetic Nephropathy: Insights on Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 37761024
- PMCID: PMC10527294
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11092583
MicroRNA-21 Silencing in Diabetic Nephropathy: Insights on Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
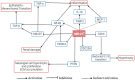
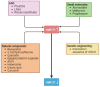
In diabetes, possibly the most significant site of microvascular damage is the kidney. Due to diabetes and/or other co-morbidities, such as hypertension and age-related nephron loss, a significant number of people with diabetes suffer from kidney diseases. Improved diabetic care can reduce the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy (DN); however, innovative treatment approaches are still required. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) is one of the most studied multipotent microRNAs (miRNAs), and it has been linked to renal fibrosis and exhibits significantly altered expression in DN. Targeting miR-21 offers an advantage in DN. Currently, miR-21 is being pharmacologically silenced through various methods, all of which are in early development. In this review, we summarize the role of miR-21 in the molecular pathogenesis of DN and several therapeutic strategies to use miR-21 as a therapeutic target in DN. The existing experimental interventions offer a way to rectify the lower miRNA levels as well as to reduce the higher levels. Synthetic miRNAs also referred to as miR-mimics, can compensate for abnormally low miRNA levels. Furthermore, strategies like oligonucleotides can be used to alter the miRNA levels. It is reasonable to target miR-21 for improved results because it directly contributes to the pathological processes of kidney diseases, including DN.
Keywords: LNA-21; antagomirs; antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs); chronic kidney disease; diabetes; hsa-miR-21; miR-21-3p; miR-21-5p; nephropathy; pharmacological silencing of miR-21; small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abarca-Gómez L., Abdeen Z.A., Hamid Z.A., Abu-Rmeileh N.M., Acosta-Cazares B., Acuin C., Adams R.J., Aekplakorn W., Afsana K., Aguilar-Salinas C.A., et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manne-Goehler J., Atun R., Stokes A., Goehler A., Houinato D., Houehanou C., Hambou M.M.S., Mbenza B.L., Sobngwi E., Balde N., et al. Diabetes Diagnosis and Care in Sub-Saharan Africa: Pooled Analysis of Individual Data from 12 Countries. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4:903–912. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30181-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Boer I.H., Caramori M.L., Chan J.C.N., Heerspink H.J.L., Hurst C., Khunti K., Liew A., Michos E.D., Navaneethan S.D., Olowu W.A., et al. Executive Summary of the 2020 KDIGO Diabetes Management in CKD Guideline: Evidence-Based Advances in Monitoring and Treatment. Kidney Int. 2020;98:839–848. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.06.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

