The Impact of Pulmonary Vein Anatomy on P-Wave Appearance during Sinus Rhythm: Cardiac Computed Tomography Study
- PMID: 37761279
- PMCID: PMC10530108
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13182911
The Impact of Pulmonary Vein Anatomy on P-Wave Appearance during Sinus Rhythm: Cardiac Computed Tomography Study
Abstract
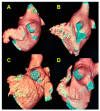
Electrocardigraphy remains a first-line evaluation method for cardiac electrical activity, recorded from the body surface. Since atrial activation is seen on the ECG as a P-wave, several factors are known to impact the appearance of the P-wave, such as the direction of electric impulse, conduction abnormalities, and anatomical characteristics of the atria. This retrospective study aimed to find statistically significant associations between the anatomy of pulmonary veins (PVs) observed in cardiac computed tomography (CT) and P-wave appearance during sinus rhythm on resting ECG. For each patient, a resting 12-lead ECG was recorded, and the field of analysis was P-wave-its duration, morphology, and axis. The evaluation of the CT scan recordings was performed by creating 3D models of the left atrium and analyzing the anatomy of the PVs and left atrial appendages (LAA). Noteworthy correlations were found: anatomy of the left PVs showed an association with LAA volume, LAA morphology, and P-wave notching in lead II. The right PVs demonstrated a relation with the P-wave axis and amplitude. Although these correlations cannot be classified as strong, the results not only expand understanding about discussed variables but also suggest the presence of a subtle and complex relationship, that warrants further exploration.
Keywords: P-wave; cardiac computed tomography; electrocardiography; left atrial appendage; pulmonary veins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Strauss D.G., Schocken D. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography. 13th ed. Wolters Kluwer Health; Waltham, MA, USA: 2020. pp. 12–13.
-
- Gettes L.S., Chung E.H. Netter’s Cardiology. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Chapter 7, Electrocardiography; pp. 43–51.
-
- Nattel S., Tomaselli G.F. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 11th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Pulmonary Vein Anatomy and Atrial Fibrillation: Implications for Catheter Ablation Strategies; pp. 1163–1190.
-
- Goldberger A.L., Goldberger Z.D., Shvilkin A. Goldberger’s Clinical Electrocardiography: A Simplified Approach. 9th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. pp. 44–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

