Medical Image Despeckling Using the Invertible Sparse Fuzzy Wavelet Transform with Nature-Inspired Minibatch Water Wave Swarm Optimization
- PMID: 37761285
- PMCID: PMC10529025
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13182919
Medical Image Despeckling Using the Invertible Sparse Fuzzy Wavelet Transform with Nature-Inspired Minibatch Water Wave Swarm Optimization
Abstract
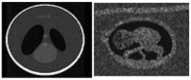
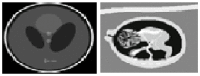
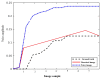
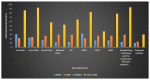
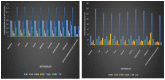
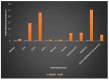
Speckle noise is a pervasive problem in medical imaging, and conventional methods for despeckling often lead to loss of edge information due to smoothing. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach that combines a nature-inspired minibatch water wave swarm optimization (NIMWVSO) framework with an invertible sparse fuzzy wavelet transform (ISFWT) in the frequency domain. The ISFWT learns a non-linear redundant transform with a perfect reconstruction property that effectively removes noise while preserving structural and edge information in medical images. The resulting threshold is then used by the NIMWVSO to further reduce multiplicative speckle noise. Our approach was evaluated using the MSTAR dataset, and objective functions were based on two contrasting reference metrics, namely the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and the mean structural similarity index metric (MSSIM). Our results show that the suggested approach outperforms modern filters and has significant generalization ability to unknown noise levels, while also being highly interpretable. By providing a new framework for despeckling medical images, our work has the potential to improve the accuracy and reliability of medical imaging diagnosis and treatment planning.
Keywords: inveritible sparse fuzzy wavelet transform; nature-inspired minibatch water wave swarm optimization; speckle noise; threshold.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this research paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
WINNet: Wavelet-Inspired Invertible Network for Image Denoising.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2022;31:4377-4392. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3184845. Epub 2022 Jul 1. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2022. PMID: 35759598
-
Despeckling of clinical ultrasound images using deep residual learning.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Oct;194:105477. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105477. Epub 2020 May 15. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32454323
-
Blind Source Parameters for Performance Evaluation of Despeckling Filters.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2016;2016:3636017. doi: 10.1155/2016/3636017. Epub 2016 May 19. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27298618 Free PMC article.
-
Edge Preserved Speckle Noise Reduction Using Integrated Fuzzy Filters.Int Sch Res Notices. 2014 Oct 30;2014:876434. doi: 10.1155/2014/876434. eCollection 2014. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014. PMID: 27437499 Free PMC article.
-
Subspace-based technique for speckle noise reduction in ultrasound images.Biomed Eng Online. 2014 Nov 25;13(1):154. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-13-154. Biomed Eng Online. 2014. PMID: 25421914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shabana Sulthana S.L., Sucharitha M. Kinetic Gas Molecule Optimization (KGMO)-Based Speckle Noise Reduction in Ultrasound Images. Soft Comput. Signal Process. 2022;10:447–455.
-
- Karaoğlu O., Bilge H.Ş., Uluer İ. Removal of speckle noises from ultrasound images using five different deep learning networks. EST. 2022;29:101030. doi: 10.1016/j.jestch.2021.06.010. - DOI
-
- Shereena V.B., Raju G. Modified non-local means model for speckle noise reduction in ultrasound images. Congr. Intell. Syst. 2022;10:691–707.
-
- Jayasingh R., RJS J.K., Telagathoti D.B., Sagayam K.M., Pramanik S., Jena O.P., Bandyopadhyay S.K. Speckle noise removal by SORAMA segmentation in Digital Image Processing to facilitate precise robotic surgery. Int. J. Reliab. Qual. E-Healthc. 2022;11:1–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources