New Immunohistochemical Markers for Pleural Mesothelioma Subtyping
- PMID: 37761312
- PMCID: PMC10529020
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13182945
New Immunohistochemical Markers for Pleural Mesothelioma Subtyping
Abstract
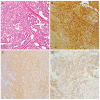
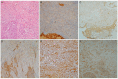
Pleural mesothelioma (PM) comprises three main subtypes: epithelioid, biphasic and sarcomatoid, which have different impacts on prognosis and treatment definition. However, PM subtyping can be complex given the inter- and intra-tumour morphological heterogeneity. We aim to use immunohistochemistry (IHC) to evaluate five markers (Mesothelin, Claudin-15, Complement Factor B, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 and p21-activated Kinase 4), whose encoding genes have been previously reported as deregulated among PM subtypes. Immunohistochemical expressions were determined in a case series of 73 PMs, and cut-offs for the epithelioid and non-epithelioid subtypes were selected. Further validation was performed on an independent cohort (30 PMs). For biphasic PM, the percentage of the epithelioid component was assessed, and IHC evaluation was also performed on the individual components separately. Mesothelin and Claudin-15 showed good sensitivity (79% and 84%) and specificity (84% and 73%) for the epithelioid subtype. CFB and PAK4 had inferior performance, with higher sensitivity (89% and 84%) but lower specificity (64% and 36%). In the biphasic group, all markers showed different expression when comparing epithelioid with sarcomatoid areas. Mesothelin, Claudin-15 and CFB can be useful in subtype discrimination. PAI1 and PAK4 can improve component distinction in biphasic PM.
Keywords: Claudin-15; Complement Factor B (CFB); Mesothelin; Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 (PAI1); immunohistochemistry; p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4); pleural mesothelioma; subtypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sauter J.B.R., Dacic S., Gill R.R. In: Thoracic Tumours. 5th ed. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, editor. Volume 5. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); Lyon, France: 2021. pp. 204–219.
-
- Husain A.N., Colby T.V., Ordonez N.G., Allen T.C., Attanoos R.L., Beasley M.B., Butnor K.J., Chirieac L.R., Churg A.M., Dacic S., et al. Guidelines for Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma 2017 Update of the Consensus Statement From the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018;142:89–108. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0124-RA. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verma V., Ahern C.A., Berlind C.G., Lindsay W.D., Shabason J., Sharma S., Culligan M.J., Grover S., Friedberg J.S., Simone C.B., 2nd Survival by Histologic Subtype of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and the Impact of Surgical Resection on Overall Survival. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2018;19:e901–e912. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.08.007. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

