Pyeloplasty in Children with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction and Associated Kidney Anomalies: Can a Robotic Approach Make Surgery Easier?
- PMID: 37761409
- PMCID: PMC10527626
- DOI: 10.3390/children10091448
Pyeloplasty in Children with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction and Associated Kidney Anomalies: Can a Robotic Approach Make Surgery Easier?
Abstract
Background: Robot-assisted pyeloplasty is widely used in pediatric surgery because of its well-known advantages over open or laparoscopic surgery. The aim is to explore our experience and evaluate the achievements we have made.
Methods: We evaluated patients undergoing robotic pyeloplasty from January 2016 to November 2021, including those who presented with a ureteropelvic junction obstruction associated with other anomalies of the kidney. The parameters examined were: age, weight, associated renal malformations, conversion rate, operative time, and intra- and postoperative complications.
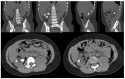
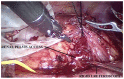
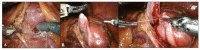
Results: Of 39 patients, 7 (20%) were included, of whom 5 (71%) were male and 2 (29%) were female. The mean age at surgery was 84 months (range 36-180 months), and the mean weight at surgery was 24.4 kg (range 11-40 kg). In five (71%) patients the ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) was left-sided and in two (29%) it was right-sided. In four (57%) cases, UPJO was associated with a horseshoe kidney, right-sided in one (25%) patient, and left-sided in the other three (75%). A 180° rotation of the kidney was present in one (14%) patient. Nephrolithiasis was present in two (29%) patients. The mean operative time was 160 min (range 140-240 min). The average bladder catheter dwell time was 1 day (range 2-3 days), while the average abdominal drainage dwell time was 2 days (range 2-4 days). The mean hospitalization time was 4 days (range 3-9 days). On average, after 45 days (range 30-65) the JJ ureteral stent was removed cystoscopically. No intraoperative complications were reported, while one case of persistent macrohematuria with anemia requiring blood transfusion occurred postoperatively.
Conclusions: Ureteropelvic junction obstruction might be associated with other congenital urinary tract anomalies such as a duplicated collecting system, horseshoe kidney, or pelvic kidney. These kinds of malformations can complicate surgery and require more attention and accuracy from the surgeon. Our experience shows that, with regards to the robotic learning curve required for pyeloplasty, the treatment of the ureteropelvic junction in these situations does not present insurmountable difficulties nor is burdened by complications. The application of robot-assisted surgery in pediatric urology makes difficult pyeloplasties easier.
Keywords: horseshoe kidney; nephrolithiasis; pediatric surgery; renal anomalies; robot-assisted pyeloplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brunhara J.A., Moscardi P.R.M., Mello M.F., Andrade H.S., Carvalho P.A.D., Cezarino B.N., Dénes F.T., Lopes R.I. Transperitoneal laparoscopic pyeloplasty in children: Does upper urinary tract anomalies affect surgical outcomes? Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018;44:370–377. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2017.0224. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Winoker J.S., Wu W.J., Matlaga B.R. Diseases and Comorbid Conditions Predisposing Children to Kidney Stones. In: Paloian N.J., Penniston K.L., editors. Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Nephrolithiasis. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

