Investigating the Role of Serum and Plasma IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-alpha, CRP, and S100B Concentrations in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosis
- PMID: 37762178
- PMCID: PMC10530258
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241813875
Investigating the Role of Serum and Plasma IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-alpha, CRP, and S100B Concentrations in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosis
Abstract
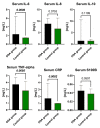
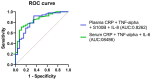
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent and underdiagnosed condition associated with cardiovascular diseases, depression, accidents, and stroke. There is an increasing need for alternative diagnostic tools beyond overnight sleep studies that measure the Apnea/Hypopnea Index (AHI). In this single-center, case-control study, we evaluated serum and plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-α, CRP, and S100B in 80 subjects, including 52 OSA patients (27 moderate [15 ≤ AHI ˂ 30], 25 severe [AHI ≥ 30]) and 28 non-OSA controls (AHI 0-5). Participants with OSA showed approximately 2 times higher median concentrations of CRP in plasma, and IL-6 in serum, as well as 1.3 to 1.7 times higher concentrations of TNF-α and IL-8 in plasma compared with the control group. Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to evaluate the predictive capabilities of these serum and plasma biomarkers in distinguishing between the OSA and control groups, revealing varying sensitivity and specificity. In summary, in this study, serum and plasma biomarkers CRP, S100B, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-8 have been shown to be elevated in patients with OSA, correlated positively with disease severity, age, and BMI. These results support the potential role of these biomarkers in diagnosing OSA, supplementing traditional methods such as overnight sleep studies.
Keywords: biomarkers; obstructive sleep apnea; plasma and serum concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osteoprotegerin, Chitinase 3-like Protein 1, and Cardiotrophin-1 as Potential Biomarkers of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults-A Case-Control Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 30;24(3):2607. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032607. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768925 Free PMC article.
-
Serum S100A12 and S100B proteins are independent predictors of the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnea.Turk J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 18;49(3):746-754. doi: 10.3906/sag-1806-147. Turk J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035738 Free PMC article.
-
[Validation of NoSAS Score and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome Screening Model for Female Snorers in Females with Obstructive Sleep Apnea].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019 Dec 30;41(6):825-831. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11131. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31907135 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of Blood Levels of C-Reactive Protein Marker in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;11(4):362. doi: 10.3390/life11040362. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Diagnostic and Monitoring Biomarkers of Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):60. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010060. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36614858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The common link between sleep apnea syndrome and osteoarthritis: a literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 21;11:1401309. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1401309. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39234045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Letter to the editor in response to "S100B as a predictor of delirium in critically ill obstetric patients: A nested case-control study".Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2024 Apr-Jun;14(2):115-116. doi: 10.4103/ijciis.ijciis_3_24. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2024. PMID: 39005977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ferritin is a potential marker of cardiometabolic risk in adolescents and young adults with sleep-disordered breathing.Sleep Adv. 2024 Jul 18;5(1):zpae048. doi: 10.1093/sleepadvances/zpae048. eCollection 2024. Sleep Adv. 2024. PMID: 39161746 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally Invasive vs. Open Synovectomy in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights into Clinical Recovery, Systemic Inflammation, and Economic Impact.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 24;14(5):1519. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051519. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40094963 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of intestinal microorganisms that affect the improvement of muscle strength.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 18;15(1):30179. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15222-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40825820 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

