Foveal Hypoplasia in CRB1-Related Retinopathies
- PMID: 37762234
- PMCID: PMC10531165
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241813932
Foveal Hypoplasia in CRB1-Related Retinopathies
Abstract
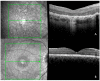
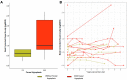
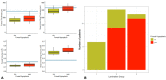
The CRB1 gene plays a role in retinal development and its maintenance. When disrupted, it gives a range of phenotypes such as early-onset severe retinal dystrophy/Leber congenital amaurosis (EOSRD/LCA), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), cone-rod dystrophy (CORD) and macular dystrophy (MD). Studies in CRB1 retinopathies have shown thickening and coarse lamination of retinal layers resembling an immature retina. Its role in foveal development has not yet been described; however, this retrospective study is the first to report foveal hypoplasia (FH) presence in a CRB1-related retinopathy cohort. Patients with pathogenic biallelic CRB1 variants from Moorfields Eye Hospital, London, UK, were collected. Demographic, clinical data and SD-OCT analyses with FH structural grading were performed. A total of 15 (48%) patients had EOSRD/LCA, 11 (35%) MD, 3 (9%) CORD and 2 (6%) RP. FH was observed in 20 (65%; CI: 0.47-0.79) patients, all of whom were grade 1. A significant difference in BCVA between patients with FH and without was found (p = 0.014). BCVA continued to worsen over time in both groups (p < 0.001), irrespective of FH. This study reports FH in a CRB1 cohort, supporting the role of CRB1 in foveal development. FH was associated with poorer BCVA and abnormal retinal morphology. Nonetheless, its presence did not alter the disease progression.
Keywords: Crumbs cell polarity complex component 1 gene (CRB1); LCA; cone-rod dystrophy (CORD); early-onset severe retinal dystrophy; foveal hypoplasia (FH); macular dystrophy (MD); optical coherence tomography (OCT); retinal dystrophy; retinitis pigmentosa (RP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nguyen X.-T., Talib M., van Schooneveld M.J., Wijnholds J., van Genderen M.M., Schalij-Delfos N.E., Klaver C.C., Talsma H.E., Fiocco M., Florijn R.J., et al. CRB1-Associated Retinal Dystrophies: A Prospective Natural History Study in Anticipation of Future Clinical Trials. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022;234:37–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2021.07.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Talib M., Van Cauwenbergh C., De Zaeytijd J., Van Wynsberghe D., De Baere E., Boon C.J.F., Leroy B.P. CRB1-associated retinal dystrophies in a Belgian cohort: Genetic characteristics and long-term clinical follow-up. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022;106:696–704. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-316781. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Varela M.D., Georgiou M., Alswaiti Y., Kabbani J., Fujinami K., Fujinami-Yokokawa Y., Khoda S., Mahroo O.A., Robson A.G., Webster A.R., et al. CRB1-Associated Retinal Dystrophies: Genetics, Clinical Characteristics, and Natural History. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2023;246:107–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2022.09.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jacobson S.G., Cideciyan A.V., Aleman T.S., Pianta M.J., Sumaroka A., Schwartz S.B., Smilko E.E., Milam A.H., Sheffield V.C., Stone E.M. Crumbs homolog 1 (CRB1) mutations result in a thick human retina with abnormal lamination. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003;12:1073–1078. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg117. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Henderson R.H., Mackay D.S., Li Z., Moradi P., Sergouniotis P., Russell-Eggitt I., Thompson D.A., Robson A.G., Holder G.E., Webster A.R., et al. Phenotypic variability in patients with retinal dystrophies due to mutations in CRB1. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011;95:811–817. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2010.186882. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

