Metallomic Signatures of Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 37762552
- PMCID: PMC10532173
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241814250
Metallomic Signatures of Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
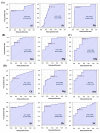
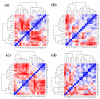
Lung cancer (LC) is the leading cause of cancer deaths, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase LC risk. Metallomics may provide insights into both of these tobacco-related diseases and their shared etiology. We conducted an observational study of 191 human serum samples, including those of healthy controls, LC patients, COPD patients, and patients with both COPD and LC. We found 18 elements (V, Al, As, Mn, Co, Cu, Zn, Cd, Se, W, Mo, Sb, Pb, Tl, Cr, Mg, Ni, and U) in these samples. In addition, we evaluated the elemental profiles of COPD cases of varying severity. The ratios and associations between the elements were also studied as possible signatures of the diseases. COPD severity and LC have a significant impact on the elemental composition of human serum. The severity of COPD was found to reduce the serum concentrations of As, Cd, and Tl and increased the serum concentrations of Mn and Sb compared with healthy control samples, while LC was found to increase Al, As, Mn, and Pb concentrations. This study provides new insights into the effects of LC and COPD on the human serum elemental profile that will pave the way for the potential use of elements as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis. It also sheds light on the potential link between the two diseases, i.e., the evolution of COPD to LC.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; inductively coupled plasma; lung cancer; mass spectrometry; metallomics; metals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zabłocka-Słowińska K., Płaczkowska S., Prescha A., Pawełczyk K., Porębska I., Kosacka M., Pawlik-Sobecka L., Grajeta H. Serum and Whole Blood Zn, Cu and Mn Profiles and Their Relation to Redox Status in Lung Cancer Patients. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018;45:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.09.024. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

