Chest X-ray Foreign Objects Detection Using Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 37762783
- PMCID: PMC10531506
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12185841
Chest X-ray Foreign Objects Detection Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
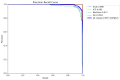
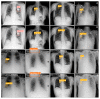
Diagnostic imaging has become an integral part of the healthcare system. In recent years, scientists around the world have been working on artificial intelligence-based tools that help in achieving better and faster diagnoses. Their accuracy is crucial for successful treatment, especially for imaging diagnostics. This study used a deep convolutional neural network to detect four categories of objects on digital chest X-ray images. The data were obtained from the publicly available National Institutes of Health (NIH) Chest X-ray (CXR) Dataset. In total, 112,120 CXRs from 30,805 patients were manually checked for foreign objects: vascular port, shoulder endoprosthesis, necklace, and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Then, they were annotated with the use of a computer program, and the necessary image preprocessing was performed, such as resizing, normalization, and cropping. The object detection model was trained using the You Only Look Once v8 architecture and the Ultralytics framework. The results showed not only that the obtained average precision of foreign object detection on the CXR was 0.815 but also that the model can be useful in detecting foreign objects on the CXR images. Models of this type may be used as a tool for specialists, in particular, with the growing popularity of radiology comes an increasing workload. We are optimistic that it could accelerate and facilitate the work to provide a faster diagnosis.
Keywords: artifacts; artificial intelligence; chest X-ray; convolutional neural network; foreign body.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis detection in chest radiograph using convolutional neural network architecture and explainable artificial intelligence.Neural Comput Appl. 2022 Apr 19:1-21. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07258-6. Online ahead of print. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 35462630 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray image phase features for improved diagnosis of COVID-19 using convolutional neural network.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Feb;16(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02305-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33420641 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Overlaid Foreign Objects in Chest X-rays-Clinical Significance and Artificial Intelligence Tools.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;11(3):308. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030308. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Pixels to Pathology: Employing Computer Vision to Decode Chest Diseases in Medical Images.Cureus. 2023 Sep 20;15(9):e45587. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45587. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37868395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep-Learning-Based Automated Rotator Cuff Tear Screening in Three Planes of Shoulder MRI.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;13(20):3254. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203254. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892075 Free PMC article.
-
The two-stage detection-after-segmentation model improves the accuracy of identifying subdiaphragmatic lesions.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25414. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76450-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455821 Free PMC article.
-
Quality control system for patient positioning and filling in meta-information for chest X-ray examinations.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1007/s11548-025-03468-0. Online ahead of print. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2025. PMID: 40531386
-
Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging and Image Processing-A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 14;16(10):1870. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101870. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791949 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic measurement of X-ray radiographic parameters based on cascaded HRNet model from the supraspinatus outlet radiographs.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Feb 1;15(2):1425-1438. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1373. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 39995702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murphy K. The Global Innovation Index 2019. How Data Will Improve Healthcare Without Adding Staff or Beds. [(accessed on 12 July 2023)]. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_pub_gii_2019-chapter8.pdf.
-
- Rogers M. Routine Admission CXR (RACXR). Core EM. [(accessed on 13 July 2023)]. Available online: https://coreem.net/core/routine-admission-cxr-racxr/
-
- Kufel J., Bargieł-Łączek K., Kocot S., Koźlik M., Bartnikowska W., Janik M., Czogalik Ł., Dudek P., Magiera M., Lis A., et al. What Is Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Networks and Deep Learning?—Examples of Practical Applications in Medicine. Diagnostics. 2023;13:2582. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152582. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghaderzadeh M., Aria M., Hosseini A., Asadi F., Bashash D., Abolghasemi H. A Fast and Efficient CNN Model for B-ALL Diagnosis and Its Subtypes Classification Using Peripheral Blood Smear Images. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022;37:5113–5133. doi: 10.1002/int.22753. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

