Association between the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Chronic Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 37762893
- PMCID: PMC10531521
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12185952
Association between the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Chronic Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
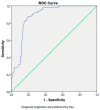
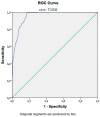
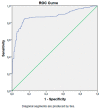
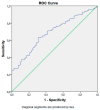
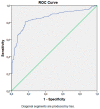
The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) is associated with inflammatory conditions. Since type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its microvascular complications produce a significant inflammatory burden, we aimed to compare the PNI levels of the subjects with T2DM to those of healthy individuals. Furthermore, we aimed to compare the PNI levels of the diabetic subjects, with and without microvascular complications. The study cohort consisted of T2DM patients and healthy volunteers. The general characteristics, laboratory data, and PNI of the T2DM and control groups were compared. We further compared the PNI levels of the diabetic patients, with and without diabetic microvascular complications. The PNI levels of the T2DM patients and the control group were 51.6 (30.1-73.8)% and 64.8 (49.4-76)%, respectively (p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses revealed that the PNI was lower in the diabetic subjects with diabetic microvascular complications than in the diabetic patients without microvascular complications (p < 0.001), in patients with diabetic nephropathy compared to those without nephropathy (p < 0.001), in patients with diabetic retinopathy compared to those without retinopathy (p < 0.001), and in patients with diabetic neuropathy compared to those without neuropathy (p < 0.001). In conclusion, we assert that assessing the PNI may yield additional diagnostic value in regards to the timely determination of diabetic microvascular complications.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; diabetic neuropathy; diabetic retinopathy; inflammation; prognostic nutritional index; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential Association Between Atherogenic Coefficient, Prognostic Nutritional Index, and Various Obesity Indices in Diabetic Nephropathy.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 14;17(8):1339. doi: 10.3390/nu17081339. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40284203 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Microvascular Complications.Cureus. 2023 May 16;15(5):e39076. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39076. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37323312 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nutritional index as a novel marker for diabetic retinopathy in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct 14;36(3):322-326. doi: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_63_22. eCollection 2022 Jul-Sep. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36276247 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):117-124. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190502103733. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31057114 Review.
-
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes using Hemoglobin A1c: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic cutpoint based on microvascular complications.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Mar;58(3):279-300. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01606-5. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33141338 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between serum globulins and diabetes mellitus in American latent tuberculosis infection patients: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 4;103(40):e39949. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039949. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465722 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the link: Hemogram-derived markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jul 15;16(7):105233. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.105233. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40697587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01637-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 38982402 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary PART1 and PLA2R1 Could Potentially Serve as Diagnostic Markers for Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Dec 27;16:4215-4231. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S445341. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 38162802 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling FOS as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker and Emetine as a Prospective Therapeutic Agent for Diabetic Nephropathy.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 13;16:6139-6153. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S435596. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38107383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demirkol M.E., Aktas G. C-reactive protein to LymphocytE count ratio could be a reliable mArkeR of thyroiditis; the CLEAR-T study. Precis. Med. Sci. 2022;11:31–34. doi: 10.1002/prm2.12065. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources