Constipation as a Drug-Related Adverse Effect in Patients with Hyperkalemia: Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate versus Conventional Potassium Binders
- PMID: 37762911
- PMCID: PMC10531607
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12185971
Constipation as a Drug-Related Adverse Effect in Patients with Hyperkalemia: Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate versus Conventional Potassium Binders
Abstract
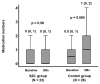
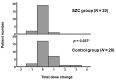
(1) Background: Constipation is one of the most serious adverse effects of potassium-lowering agents and decreases patients' quality of life. Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (SZC) is a recently innovated potassium binder intended for patients with hyperkalemia. The impact of SZC on the worsening of constipation, as compared with conventional potassium binders, remains unknown. (2) Methods: Patients with hyperkalemia who continued SZC for over 3 months between July 2020 and May 2022 were included in this retrospective study. Patients who received other conventional potassium binders during the same period were included as a control group. Trends in the doses of anti-constipation agents during the 3-month therapeutic period were compared between the two groups as a surrogate for worsening constipation. (3) Results: A total of 50 patients (median age 74 years, 31 male) were included, consisting of 22 patients with SZC and 28 patients with other conventional potassium binders. All patients had hyperkalemia and chronic kidney disease at baseline. During the 3-month therapeutic period, serum potassium levels decreased significantly in both groups (p < 0.05 for both). The number of anti-constipation remained unchanged in the SZC group but tended to increase in the control group (p = 0.56 and p = 0.090, respectively). The total dose change in all anti-constipations was significantly lower in the SZC group than in the control group (p = 0.037). (4) Conclusions: Conventional potassium binders have a tendency to worsen constipation, whereas SZC may have the potential to improve hyperkalemia without worsening constipation. SZC may be recommended, particularly in elderly patients with ongoing or high-risk constipation.
Keywords: heart failure; potassium; renal failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single Dose of Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate Versus Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate in Hospitalized Patients With Hyperkalemia.Ann Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;57(9):1044-1052. doi: 10.1177/10600280221141918. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Ann Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36637028
-
Effects and Safety of a Novel Oral Potassium-Lowering Drug-Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate for the Treatment of Hyperkalemia: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Oct;35(5):1057-1066. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07134-2. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 33459923 Free PMC article.
-
Serum potassium response to single-dose sodium zirconium cyclosilicate for the treatment of asymptomatic hyperkalemia in hospitalized patients.Pharmacotherapy. 2024 Jan;44(1):13-21. doi: 10.1002/phar.2854. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Pharmacotherapy. 2024. PMID: 37475499
-
Management of hyperkalemia in chronic heart failure using sodium zirconium cyclosilicate.Clin Cardiol. 2021 Sep;44(9):1272-1275. doi: 10.1002/clc.23683. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Clin Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34263946 Free PMC article.
-
Patiromer and Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate in Treatment of Hyperkalemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2021 Jul 5;95:100635. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2021.100635. eCollection 2021. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2021. PMID: 34367383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety assessment of sodium zirconium cyclosilicate: A FAERS-based disproportionality analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 25;20(3):e0320585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320585. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40132024 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the top 30 drugs associated with drug-induced constipation based on the FDA adverse event reporting system.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 2;15:1443555. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1443555. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39286628 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Gastrointestinal Motility and Worsening Heart Failure in Patients Receiving Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Replacement.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 23;13(15):4301. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154301. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narita Y., Fukumoto K., Fukunaga M., Kondo Y., Ishitsuka Y., Jono H., Irie T., Saito H., Kadowaki D., Hirata S. Comparative Study of Constipation Exacerbation by Potassium Binders Using a Loperamide-Induced Constipation Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:2491. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072491. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

