The Effectiveness of Adductor Canal Block Compared to Femoral Nerve Block on Readiness for Discharge in Patients Undergoing Outpatient Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Multi-Center Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37762959
- PMCID: PMC10531554
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12186019
The Effectiveness of Adductor Canal Block Compared to Femoral Nerve Block on Readiness for Discharge in Patients Undergoing Outpatient Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Multi-Center Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
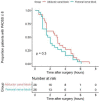
This study evaluated the effect of adductor canal block (ACB) versus femoral nerve block (FNB) on readiness for discharge in patients undergoing outpatient anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. We hypothesized that ACB would provide sufficient pain relief while maintaining motor strength and safety, thus allowing for earlier discharge. This was a randomized, multi-center, superiority trial. From March 2014 to July 2017, patients undergoing ACL reconstruction were enrolled. The primary outcome was the difference in readiness for discharge, defined as Post-Anesthetic Discharge Scoring System score ≥ 9. Twenty-six patients were allocated to FNB and twenty-seven to ACB. No difference in readiness for discharge was found (FNB median 1.8 (95% CI 1.0 to 3.5) vs. ACB 2.9 (1.5 to 4.7) hours, p = 0.3). Motor blocks and (near) falls were more frequently reported in patients with FNB vs. ACB (20 (76.9%) vs. 1 (3.7%), p < 0.001, and 7 (29.2%) vs. 1 (4.0%), p = 0.023. However, less opioids were consumed in the post-anesthesia care unit for FNB (median 3 [0, 21] vs. 15 [12, 42.5] oral morphine milligram equivalents, p = 0.004) for ACB. Between patients with FNB or ACB, no difference concerning readiness for discharge was found. Despite a slight reduction in opioid consumption immediately after surgery, FNB demonstrates a less favorable safety profile compared to ACB, with more motor blocks and (near) falls.
Keywords: analgesics; anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction; nerve block; opioid; pain; postoperative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adductor Canal Block Provides Noninferior Analgesia and Superior Quadriceps Strength Compared with Femoral Nerve Block in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.Anesthesiology. 2016 May;124(5):1053-64. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001045. Anesthesiology. 2016. PMID: 26938989 Clinical Trial.
-
Quadriceps Strength Deficits After a Femoral Nerve Block Versus Adductor Canal Block for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Prospective, Single-Blinded, Randomized Trial.Orthop J Sports Med. 2018 Sep 26;6(9):2325967118797990. doi: 10.1177/2325967118797990. eCollection 2018 Sep. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 30276220 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Adductor Canal Block Versus Femoral Nerve Block on Quadriceps Strength, Function, and Postoperative Pain After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Level 1 Studies.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Jul;48(9):2305-2313. doi: 10.1177/0363546519883589. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31800300
-
Adductor Canal Block Versus Femoral Nerve Block for Pain Control After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Prospective Randomized Trial.Am J Sports Med. 2019 Feb;47(2):355-363. doi: 10.1177/0363546518815874. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Am J Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 30557034 Clinical Trial.
-
Adductor Canal Versus Femoral Nerve Block after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Level I Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing Early Postoperative Pain, Opioid Requirements, and Quadriceps Strength.Arthroscopy. 2020 Jul;36(7):1973-1980. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.03.040. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Arthroscopy. 2020. PMID: 32315764
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Effects of Adductor Canal and Femoral Nerve Blocks on Postoperative Opioid Consumption and Inflammatory Factor Levels in Elderly Patients After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Observational Study.J Pain Res. 2024 Jul 11;17:2375-2391. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S463097. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39011277 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of the effects of sciatic nerve block combined with continuted femoral nerve block or continuted adductor canal block on pain and motor function after total knee arthroplasty].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;38(5):556-561. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202402048. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38752241 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Local Infiltration Analgesia Versus Adductor Canal Block for Managing Pain After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Orthop J Sports Med. 2024 Nov 12;12(11):23259671241292029. doi: 10.1177/23259671241292029. eCollection 2024 Nov. Orthop J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39534393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

