Depiction of Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) in Diabetes with a Focus on Diabetic Microvascular Complications
- PMID: 37762992
- PMCID: PMC10531730
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12186053
Depiction of Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) in Diabetes with a Focus on Diabetic Microvascular Complications
Abstract
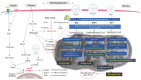
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) still holds the title as one of the most debilitating chronic diseases with rising prevalence and incidence, including its complications such as retinal, renal, and peripheral nerve disease. In order to develop novel molecules for diagnosis and treatment, a deep understanding of the complex molecular pathways is imperative. Currently, the existing agents for T2DM treatment target only blood glucose levels. Over the past decades, specific building blocks of proteins-branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) including leucine, isoleucine, and valine-have gained attention because they are linked with insulin resistance, pre-diabetes, and diabetes development. In this review, we discuss the hypothetical link between BCAA metabolism, insulin resistance, T2DM, and its microvascular complications including diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy. Further research on these amino acids and their derivates may eventually pave the way to novel biomarkers or therapeutic concepts for the treatment of diabetes and its accompanied complications.
Keywords: BCAAs; T2DM; branched chain amino acids; diabetes mellitus; diabetic nephropathy; diabetic retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ramzan I., Ardavani A., Vanweert F., Mellett A., Atherton P.J., Idris I. The Association between Circulating Branched Chain Amino Acids and the Temporal Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022;14:4411. doi: 10.3390/nu14204411. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

