Comparison between Sugammadex and Neostigmine after Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery-Thymectomy in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis: A Single-Center Retrospective Exploratory Analysis
- PMID: 37763148
- PMCID: PMC10533017
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13091380
Comparison between Sugammadex and Neostigmine after Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery-Thymectomy in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis: A Single-Center Retrospective Exploratory Analysis
Abstract
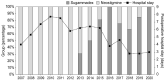
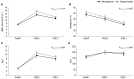
This single-center retrospective exploratory analysis evaluated the effects of sugammadex compared with neostigmine on postoperative recovery in patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) who underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)-thymectomy. This retrospective study included 180 patients with MG, aged >18 years, who received sugammadex (sugammadex group, n = 83) or neostigmine-glycopyrrolate (neostigmine group, n = 88) after VATS-thymectomy between November 2007 and December 2020. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) adjustment was performed to balance the baseline characteristics between the two groups. The primary outcome was the length of postoperative hospital stay, and the secondary outcomes were the incidence of postoperative mortality and complications, as well as the postoperative extubation and reintubation rates, in the operating room after VATS-thymectomy; the outcomes were compared between the two groups. After IPTW adjustment, the sugammadex group showed a significantly shorter median postoperative hospital stay than the neostigmine group (4 (2, 4) vs. 5 (3, 6) days, respectively; p = 0.003). There were no significant differences between the two groups in the incidences of postoperative complications (including postoperative myasthenic crisis, nerve palsy, atelectasis, and pleural effusion). Patients with MG following VATS-thymectomy who received sugammadex showed a significantly shorter postoperative hospital stay than those who received neostigmine.
Keywords: myasthenia gravis; neostigmine; sugammadex; thymectomy; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Sugammadex on Postoperative Myasthenic Crisis in Myasthenia Gravis Patients: Propensity Score Analysis of a Japanese Nationwide Database.Anesth Analg. 2020 Feb;130(2):367-373. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004239. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 31124838
-
Comparison of postoperative pulmonary complications between sugammadex and neostigmine in lung cancer patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy: a prospective double-blinded randomized trial.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021 Jan;16(1):60-67. doi: 10.17085/apm.20056. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 33486942 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous ventilation thoracoscopic thymectomy without muscle relaxant for myasthenia gravis: Comparison with "standard" thoracoscopic thymectomy.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018 Apr;155(4):1882-1889.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.11.045. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 29249499
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery thymectomy versus open thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis: a meta-analysis.Acta Chir Belg. 2016 Oct;116(5):282-288. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2016.1176419. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Acta Chir Belg. 2016. PMID: 27426672 Review.
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery or transsternal thymectomy in the treatment of myasthenia gravis?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011 Jan;12(1):40-6. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2010.251041. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011. PMID: 20943831 Review.
Cited by
-
Sugammadex versus cholinesterase inhibitors to antagonize respiratory dysfunction after neuromuscular blockade in patients undergoing pulmonary surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Perioper Med (Lond). 2025 Jul 10;14(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13741-025-00557-1. Perioper Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40635027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of sugammadex in management of patients with myasthenia gravis undergoing general anesthesia: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 8;11(2):e41757. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41757. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39882471 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Sugammadex and Neostigmine: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Past 15 Years.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 29;19:6357-6377. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S519235. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40761668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van den Bersselaar L.R., Gubbels M., Riazi S., Heytens L., Jungbluth H., Voermans N.C., Snoeck M.M.J. Mapping the current evidence on the anesthetic management of adult patients with neuromuscular disorders-a scoping review. Can. J. Anaesth. 2022;69:756–773. doi: 10.1007/s12630-022-02230-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bom A., Bradley M., Cameron K., Clark J.K., Van Egmond J., Feilden H., MacLean E.J., Muir A.W., Palin R., Rees D.C., et al. A novel concept of reversing neuromuscular block: Chemical encapsulation of rocuronium bromide by a cyclodextrin-based synthetic host. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002;41:266–270. doi: 10.1002/1521-3757(20020118)114:2<275::AID-ANGE275>3.0.CO;2-A. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

