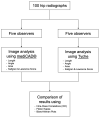
A Novel Tool for Collaborative and Blinded Orthopedic Image Analysis
- PMID: 37763209
- PMCID: PMC10532740
- DOI: 10.3390/life13091805
A Novel Tool for Collaborative and Blinded Orthopedic Image Analysis
Abstract
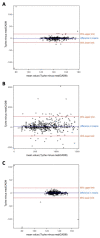
Image analysis plays a central role in orthopedics and research but comes with many challenges, including anonymization, bias, and achieving efficient analyses using multiple independent observers. Appropriate software is still lacking. Tyche is a free online tool that displays images in a random order without showing any metadata. Additionally, when using Tyche, observers can store results in the same window, and the final results are immediately visible to the project manager. In this study, we compared results from Tyche with those from a validated tool. One hundred pelvic radiographs were analyzed separately by five orthopedic surgeons using both Tyche and the validated software. Common orthopedic measurement modalities and scores were determined. The methods were compared using intra-class correlations and Fleiss' kappa coefficients as well as Bland-Altman plots. Significant correlations ranging from r = 0.17 (Kallgren and Lawrence Score) to r = 0.99 (area measurements) were calculated for inter- and intraobserver agreements between the two tools for all measurements. The Bland-Altman plots indicated the non-inferiority of either tool. The images were analyzed significantly faster when Tyche was used. We conclude that Tyche is a valid tool for use in orthopedic image analysis. Tyche could be utilized for determining inter- and intraobserver agreements, in multicenter studies and for score validations.
Keywords: Tyche; blinded image analysis; collaborative image analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interest/personal relationships which may be considered potential competing interest: the first author invented and created “Tyche”. No funding of any kind was received.
Figures


References
-
- Osoba O., Welser W. An Intelligence in Our Image: The Risks of Bias and Errors in Artificial Intelligence. Rand Corporation; Santa Monica, CA, USA: 2017. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

