Medication Overuse Headaches among Children-The Contribution of Migraine and TTH
- PMID: 37763306
- PMCID: PMC10532859
- DOI: 10.3390/life13091902
Medication Overuse Headaches among Children-The Contribution of Migraine and TTH
Abstract
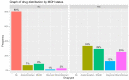
Medication overuse headaches are a frequent phenomenon observed in individuals suffering from chronic headaches. It arises due to the excessive consumption of pain-relief medications, resulting in the escalation and continuous persistence of headache symptoms. Nevertheless, the prevalence and distinctive characteristics of medication overuse headaches in the pediatric population have not been comprehensively explored. The primary objective of this research is to delineate the features of medication overuse headaches in children, particularly emphasizing the investigation of its epidemiology and the diagnostic patterns for headaches. We conducted a retrospective study and analyzed the medical records of children and adolescents who were evaluated at the outpatient pediatric headache clinic at the Bnai Zion Medical Center for headaches during the period spanning 2007 to 2017. Our study encompassed a cohort of 1008 patients experiencing headaches. Among these participants, 268 individuals (26.6%) were diagnosed with migraine, 250 (24.8%) exhibited tension-type headaches (TTH), and 490 (48.6%) were classified as having undifferentiated headaches. Out of the whole group, 65 had chronic headaches: 35 (54%) with migraine, 20 (30%) with tension-type headaches (TTH), and 10 (15%) with the undifferentiated headache of childhood, with the majority (73%) being female. In summary, medication overuse headaches are a prevalent issue among children grappling with chronic headaches. Intriguingly, they appear to be more pronounced within the tension-type headache (TTH) group compared to migraine sufferers and exhibit a higher prevalence among females. This study underscores the significance of early detection and careful management of medication overuse headaches in pediatric cases, shedding light on its distinct characteristics in the realm of childhood headache disorders. Further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying factors contributing to the observed gender disparity and the distinct prevalence rates among different headache subtypes.
Keywords: TTH; children; medication overuse headache; migraine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Risk Factors in Patients With Chronic Daily Headache and Medication-Overuse Headache.Brain Behav. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70407. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70407. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40079498 Free PMC article.
-
Headache characteristics and chronification of migraine and tension-type headache: A population-based study.Cephalalgia. 2010 Aug;30(8):943-52. doi: 10.1177/0333102409357958. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Cephalalgia. 2010. PMID: 20656705
-
Subsume Pediatric Headaches in Psychiatric Disorders? Critiques on Delphic Nosology, Diagnostic Conundrums, and Variability in the Interventions.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Jul;28(7):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01225-7. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38367199 Review.
-
Pediatric mixed headache -The relationship between migraine, tension-type headache and learning disabilities - in a clinic-based sample.J Headache Pain. 2016;17:42. doi: 10.1186/s10194-016-0625-x. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Headache Pain. 2016. PMID: 27102119 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Migraine and Other Types of Primary Headache in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neuroepidemiology. 2025 Feb 25:1-11. doi: 10.1159/000543086. Online ahead of print. Neuroepidemiology. 2025. PMID: 39999811
Cited by
-
Expert opinion on heat therapy for teenagers' musculoskeletal pain management.Ann Transl Med. 2024 Oct 20;12(5):84. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-1931. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Ann Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39507458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Find N.L., Terlizzi R., Munksgaard S.B., Bendtsen L., Tassorelli C., Nappi G., Katsarava Z., Lainez M., Goicochea M.T., Shand B., et al. Medication Overuse Headache in Europe and Latin America: General Demographic and Clinical Characteristics, Referral Pathways and National Distribution of Painkillers in a Descriptive, Multinational, Multicenter Study. J. Headache Pain. 2015;17:20. doi: 10.1186/s10194-016-0612-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources