Exploring Small-Diameter Melanomas: A Retrospective Study on Clinical and Dermoscopic Features
- PMID: 37763310
- PMCID: PMC10533118
- DOI: 10.3390/life13091907
Exploring Small-Diameter Melanomas: A Retrospective Study on Clinical and Dermoscopic Features
Abstract
Background: Early melanoma detection allows for timely intervention and treatment, significantly improving the chances of favorable outcomes for patients. Small-diameter melanoma (SDM) typically represents an initial growth phase of cutaneous melanoma. One of the challenges in detecting melanoma in their early stage lies in the fact that dermoscopy criteria have been primarily designed for fully developed lesions. Early-stage melanomas may be difficult to detect and possibly even be overlooked or misinterpreted during examinations.
Methods: The primary aim of this study was to identify valuable clinical and dermoscopic clues to enhance the detection of SDMs. To achieve this objective, we conducted a comprehensive retrospective analysis, including forty SDMs with a diameter of 5 mm or less. These cases were diagnosed over an 8-year period and were collected from five referral centers across Brazil. Seven experienced dermatologists independently assessed the dermoscopic features of each lesion. Additionally, this study includes demographic and histological information.
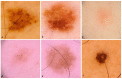
Results: The study encompassed a total of 28 patients, of which 16 were females, accounting for 58% of the participants, with an average age of 43.6 years. Among the small-diameter melanomas (SDMs) under investigation, the majority, constituting 27 cases (69.2%), were identified as "de novo" lesions, i.e., not associated with a nevus. Additionally, eight SDMs (20%) exhibited invasive characteristics, with Breslow index measurements ranging between 0.2 to 0.4 mm, suggesting an early stage of malignancy. During dermoscopic examinations, the most prevalent features observed were irregular dots and globules, present in 95% and 87.5% of cases, respectively. Moreover, brown structureless areas were identified in 70% of lesions, followed by atypical network (67.5%), pseudopods (55%), dotted vessels (47.5%), flat structureless blue-gray areas (42.5%), and irregular blotches (40%). Notably, all SDM were diagnosed in patients under surveillance through total body skin photography (TBSP) and Digital Dermoscopy (DD).
Conclusions: Dermoscopy significantly enhances the diagnostic accuracy of melanoma, even in its early stages. Particularly for high-risk patients with numerous nevi, the identification of a new lesion or subtle changes on dermoscopy during follow-up may serve as the sole clue for an early diagnosis. This emphasizes the critical role of dermoscopy in SDM detection and reinforces the importance of surveillance in high-risk patients for timely and effective management.
Keywords: dermoscopy; melanoma; micro-melanoma; mini-melanoma; small-diameter melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Megaris A., Lallas A., Bagolini L.P., Balais G., Cuevas R.G., Lallas K., Gkentsidi T., Manoli S.M., Papageorgiou C., Spyridis I., et al. Dermoscopy features of melanomas with a diameter up to 5 mm (micromelanomas): A retrospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020;83:1160–1161. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

