Polypropylene Color Masterbatches Containing Layered Double Hydroxide Modified with Quinacridone and Phthalocyanine Pigments-Rheological, Thermal and Application Properties
- PMID: 37763521
- PMCID: PMC10532881
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16186243
Polypropylene Color Masterbatches Containing Layered Double Hydroxide Modified with Quinacridone and Phthalocyanine Pigments-Rheological, Thermal and Application Properties
Abstract
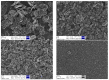
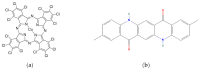
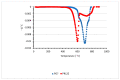
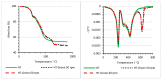
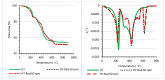
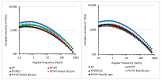
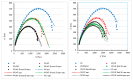
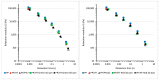
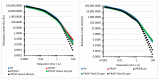
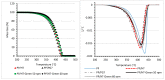
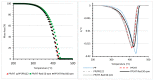
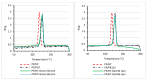
Polypropylene color masterbatches containing modified layered double hydroxides, LDHs, were created. The simple, industry-acceptable method of LDH surface modification with quinacridone and phthalocyanine pigments using the pulverization method in ball mills was applied. It was reported that the modification parameters such as time and rotational speed affected the tendency to create the aggregates for modified fillers. TGA analysis of the modified LDH showed that modification with phthalocyanine pigment shifted the temperature at which 5%, T5%, and 10% of mass loss, T10%, occurred compared with that for unmodified LDH. The viscoelastic properties of prepared masterbatches were investigated. The incorporation of the modified fillers instead of neat pigments led to an increase in the loss shear modulus, G″, indicating a stronger influence on the dissipation of energy by the melted masterbatch. The similar values of tan, δ, were determined for melted masterbatches containing phthalocyanine pigment and green modified LDH filler. The incorporation of both LDHs modified by phthalocyanine and quinacridone pigment fillers slightly increased the zero-shear viscosity, η0, compared with that of the masterbatches based on the neat pigments. The Cole-Cole plots and the analysis of the Maxwell and continuous relaxation models showed that modified colored LDH fillers facilitated the relaxation of the melted masterbatch, and shorter relaxation times were observed. The phthalocyanine-modified LDH filler improved the thermal stability of the masterbatches. Additionally, the impact of pigments and modified, colored LDH on the crystallization of polypropylene was investigated.
Keywords: layered double hydroxide; phthalocyanine pigments; polypropylene masterbatches; quinacridone pigments; viscoelastic properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rheological Properties of Polyethylene Color Masterbatches Containing Pigment RED 122 (2,9-Dimethylquinacridone) Modified by Silanes Using Pulverization Method.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;17(5):618. doi: 10.3390/polym17050618. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40076111 Free PMC article.
-
Layered Double Hydroxide (MgFeAl-LDH)-Based Polypropylene (PP) Nanocomposite: Mechanical Properties and Thermal Degradation.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;13(19):3452. doi: 10.3390/polym13193452. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641267 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of SEBS/Halloysite Masterbatch Obtained in Different Extrusion Conditions on the Properties of Hybrid Polypropylene/Glass Fiber Composites for Auto Parts.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 15;13(20):3560. doi: 10.3390/polym13203560. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685321 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Literature Review of the Effect of Layered Double Hydroxides on the Mechanical Properties of Rubber.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;13(21):3716. doi: 10.3390/polym13213716. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent innovations in functionalized layered double hydroxides: Fabrication, characterization, and industrial applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020 Sep;283:102216. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102216. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020. PMID: 32763493 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Compounding Parameters on Color Space and Properties of Thermoplastics with Ultramarine Blue Pigment.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;15(24):4718. doi: 10.3390/polym15244718. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broda J., Gawlowski A., Slusarczyk C., Wlochowicz A., Fabia J. The influence of additives on the structure of polypropylene fibres. Dye. Pigment. 2007;74:508–511. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.10.004. - DOI
-
- Paleo A.J., Krause B., Mendes A.R., Tavares C.J., Cerqueira M.F., Muňoz E., Pötschke P. Comparative thermoelectric properties of polypropylene composites melt-processed using Pytograf® III carbon nanofibers. J. Compos. Sci. 2023;7:173. doi: 10.3390/jcs7040173. - DOI
-
- Harekrushna S., Mishra B., Senapti P., Murmu R., Sahu D. Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of graphene nanoplatelet-reinforced polypropylene nanocomposites: Effects of nanofiller thickness. J. Compos. Sci. 2021;5:24. doi: 10.3390/jcs5010024. - DOI
-
- Wang Q., Zhang X., Wang C.J., Zhu J., Guo Z., O’Hare D. Polypropylene/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2012;22:19113. doi: 10.1039/c2jm33493c. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

