The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37763760
- PMCID: PMC10537482
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59091641
The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
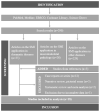
Background and Objectives: Superb microvascular imaging is an advanced Doppler algorithm that seems to be useful in detecting low-velocity blood flow without using a contrast agent. Increasing evidence suggests that SMI is a more sensitive tool than conventional Doppler techniques for evaluating rheumatic diseases, especially inflammatory arthritis. We aimed to assess the use of SMI in evaluating joints and extraarticular structures. Materials and Methods: Two reviewers independently reviewed the literature to provide a global overview of the possibilities of SMI in rheumatology. Original English-language articles published between February 2014 and November 2022 were identified through database (PubMed, Medline, Ebsco, the Cochrane Library, and ScienceDirect) searching, and analysed to summarise existing evidence according to PRISMA methodology. Inclusion criteria covered original research articles reporting applications of SMI on rheumatic diseases and musculoskeletal disorders secondary to rheumatic conditions. Qualitative data synthesis was performed. Results: A total of 18 articles were included. No systematic reviews fulfilled our inclusion criteria. Most studies focused on characterising the synovial vascularity of rheumatoid arthritis. There have been several attempts to demonstrate SMI's value for evaluating extra-articular soft tissues (fat pads or salivary glands) and large-diameter vessels. The quantitative importance of SMI vascular indices could become a useful non-invasive diagnostic marker. Studies on therapeutic applications are still scarce, and the majority of studies have gaps in reporting the methodology (ultrasound performance technique and settings) of the research. Conclusions: SMI has proved to be useful in characterising low-flow vascularity, and growing evidence indicates that SMI is a non-invasive and lower-cost tool for prognostic assessment, especially in inflammatory arthritis. Preliminary findings also suggest potential interest in evaluating the effect of treatment.
Keywords: autoimmune rheumatic diseases; low flow; microflow imaging; microvascular imaging; superb microvascular imaging; systematic review; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Niu L.J., Hao Y.Z., Zhou C.W. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in thyroid lesions. Chin. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2006;41:415s. - PubMed
-
- Klauser A., Demharter J., De Marchi A., Sureda D., Barile A., Masciocchi C., Faletti C., Schirmer M., Kleffel T., Bohndorf K. Contrast enhanced gray-scale sonography in assessment of joint vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the IACUS study group. Eur. Radiol. 2005;15:2404–2410. doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2884-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical