Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing of Gecko-Inspired Switchable Adhesion Interfaces on a Flexible Substrate
- PMID: 37763905
- PMCID: PMC10534918
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14091742
Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing of Gecko-Inspired Switchable Adhesion Interfaces on a Flexible Substrate
Abstract
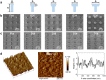
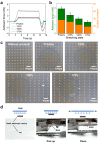
Biomimetic switchable adhesion interfaces (BSAIs) with dynamic adhesion states have demonstrated significant advantages in micro-manipulation and bio-detection. Among them, gecko-inspired adhesives have garnered considerable attention due to their exceptional adaptability to extreme environments. However, their high adhesion strength poses challenges in achieving flexible control. Herein, we propose an elegant and efficient approach by fabricating three-dimensional mushroom-shaped polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) micropillars on a flexible PDMS substrate to mimic the bending and stretching of gecko footpads. The fabrication process that employs two-photon polymerization ensures high spatial resolution, resulting in micropillars with exquisite structures and ultra-smooth surfaces, even for tip/stem ratios exceeding 2 (a critical factor for maintaining adhesion strength). Furthermore, these adhesive structures display outstanding resilience, enduring 175% deformation and severe bending without collapse, ascribing to the excellent compatibility of the micropillar's composition and physical properties with the substrate. Our BSAIs can achieve highly controllable adhesion force and rapid manipulation of liquid droplets through mechanical bending and stretching of the PDMS substrate. By adjusting the spacing between the micropillars, precise control of adhesion strength is achieved. These intriguing properties make them promising candidates for various applications in the fields of microfluidics, micro-assembly, flexible electronics, and beyond.
Keywords: mushroom-shaped micropillars; switchable adhesion; two-photon polymerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arzt E., Quan H., McMeeking R.M., Hensel R. Functional surface microstructures inspired by nature—From adhesion and wetting principles to sustainable new devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021;120:100823. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2021.100823. - DOI
-
- Gao M., Wu H., Plamthottam R., Xie Z., Liu Y., Hu J., Wu S., Wu L., He X., Pei Q. Skin temperature-triggered, debonding-on-demand sticker for a self-powered mechanosensitive communication system. Matter. 2021;4:1962–1974. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2021.03.003. - DOI
-
- Tian Y., Guan P., Wen C., Lu M., Li T., Fan L., Yang Q., Guan Y., Kang X., Jiang Y., et al. Strong Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel Adhesives with Removability and Reusability for Damaged Tissue Closure and Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022;14:54488–54499. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c14103. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

