Carbon-Based Enzyme Mimetics for Electrochemical Biosensing
- PMID: 37763909
- PMCID: PMC10538133
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14091746
Carbon-Based Enzyme Mimetics for Electrochemical Biosensing
Abstract
Natural enzymes are used as special reagents for the preparation of electrochemical (bio)sensors due to their ability to catalyze processes, improving the selectivity of detection. However, some drawbacks, such as denaturation in harsh experimental conditions and their rapid de- gradation, as well as the high cost and difficulties in recycling them, restrict their practical applications. Nowadays, the use of artificial enzymes, mostly based on nanomaterials, mimicking the functions of natural products, has been growing. These so-called nanozymes present several advantages over natural enzymes, such as enhanced stability, low cost, easy production, and rapid activity. These outstanding features are responsible for their widespread use in areas such as catalysis, energy, imaging, sensing, or biomedicine. These materials can be divided into two main groups: metal and carbon-based nanozymes. The latter provides additional advantages compared to metal nanozymes, i.e., stable and tuneable activity and good biocompatibility, mimicking enzyme activities such as those of peroxidase, catalase, oxidase, superoxide dismutase, nuclease, or phosphatase. In this review article, we have focused on the use of carbon-based nanozymes for the preparation of electrochemical (bio)sensors. The main features of the most recent applications have been revised and illustrated with examples selected from the literature over the last four years (since 2020).
Keywords: artificial enzyme; carbon nanozyme; electrochemical biosensor; enzyme mimicking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the writing of the manuscript.
Figures
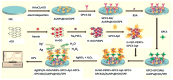

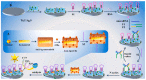
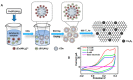
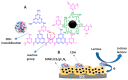

References
-
- Smutok O., Kavetskyy T., Prokopiv T., Serkiz R., Wojnarowska-Nowak R., Sausa O., Novak D., Berek A., Melman M. Gonchar, New micro/nanocomposite with peroxidase-like activity in construction of oxidases-based amperometric biosensors for ethanol and glucose analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2021;1143:201–209. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.11.052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arshad F., Arrigan D.W.M., Ahmed M.U. Recent developments in nanozyme based sensors for detection of clinical bio-markers—A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022;22:15. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3191291. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

