Neuromuscular Magnetic Field Measurement Based on Superconducting Bio-Sensors
- PMID: 37763931
- PMCID: PMC10535156
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14091768
Neuromuscular Magnetic Field Measurement Based on Superconducting Bio-Sensors
Abstract
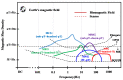
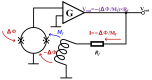
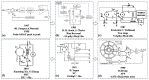
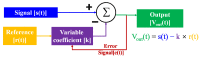
These years, disease-causing and disabling diseases have caused great concern. Neurological musculoskeletal disorders are diverse and affect people of a wide range of ages. And the lack of comprehensive diagnostic methods places a huge burden on healthcare systems and social economies. In this paper, the current status of clinical research on neuromuscular diseases is introduced, and the advantages of magnetic field measurement compared with clinical diagnostic methods are illustrated. A comprehensive description of the related technology of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs), magnetic field detection noise suppression scheme, the development trend of the sensor detection system, and the application and model establishment of the neuromuscular magnetic field is also given in this paper. The current research and development trends worldwide are compared simultaneously, and finally the conclusions and outlook are put forward. Based on the description of the existing literature and the ideas of other researchers, the next development trends and my own research ideas are presented in this paper, that is, starting from the establishment of a neuromuscular model, combining medical and industrial work, designing a sensor system that meets clinical needs, and laying the foundation for the clinical application of a bio-magnetic system. This review promotes a combination between medicine and industry, and guides researchers on considering the challenges of sensor development in terms of clinical needs. In addition, in this paper, the development trends are described, including the establishment of the model, the clinical demand for sensors, and the challenges of system development so as to give certain guidance to researchers.
Keywords: SQUID; environmental compensation; modeling; neuromuscular magnetic field; noise suppression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fine-Tuning and Optimization of Superconducting Quantum Magnetic Sensors by Thermal Annealing.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 21;19(17):3635. doi: 10.3390/s19173635. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31438525 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetoelectric Magnetic Field Sensors: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 17;21(18):6232. doi: 10.3390/s21186232. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superconducting Quantum Interferometers for Nondestructive Evaluation.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Dec 6;17(12):2798. doi: 10.3390/s17122798. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29210980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Theory meets Industry (Erwin-Schrödinger-Institute (ESI), Vienna, Austria, 12-14 June 2007).J Phys Condens Matter. 2008 Feb 13;20(6):060301. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/20/06/060301. Epub 2008 Jan 24. J Phys Condens Matter. 2008. PMID: 21693862
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
References
-
- Briggs A.M., Cross M.J., Hoy D.G., Sànchez-Riera L., Blyth F.M., Woolf A.D., March L. Musculoskeletal health conditions represent a global threat to healthy aging: A report for the 2015 World Health Organization world report on ageing and health. Gerontologist. 2016;56:S243–S255. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnw002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Briggs A.M. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

