Sour Beer as Bioreservoir of Novel Craft Ale Yeast Cultures
- PMID: 37763982
- PMCID: PMC10537276
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11092138
Sour Beer as Bioreservoir of Novel Craft Ale Yeast Cultures
Abstract
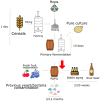
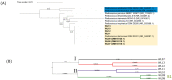
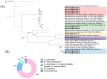
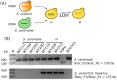
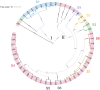
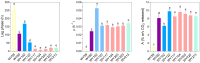
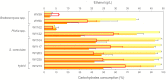
The increasing demand for craft beer is driving the search for novel ale yeast cultures from brewing-related wild environments. The focus of bioprospecting for craft cultures is to identify feral yeasts suitable to imprint unique sensorial attributes onto the final product. Here, we integrated phylogenetic, genotypic, genetic, and metabolomic techniques to demonstrate that sour beer during aging in wooden barrels is a source of suitable craft ale yeast candidates. In contrast to the traditional lambic beer maturation phase, during the aging of sour-matured production-style beer, different biotypes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae dominated the cultivable in-house mycobiota, which were followed by Pichia membranifaciens, Brettanomyces bruxellensis, and Brettanomyces anomalus. In addition, three putative S. cerevisiae × Saccharomyces uvarum hybrids were identified. S. cerevisiae feral strains sporulated, produced viable monosporic progenies, and had the STA1 gene downstream as a full-length promoter. During hopped wort fermentation, four S. cerevisiae strains and the S. cerevisiae × S. uvarum hybrid WY213 exceeded non-Saccharomyces strains in fermentative rate and ethanol production except for P. membranifaciens WY122. This strain consumed maltose after a long lag phase, in contrast to the phenotypic profile described for the species. According to the STA1+ genotype, S. cerevisiae partially consumed dextrin. Among the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by S. cerevisiae and the S. cerevisiae × S. uvarum hybrid, phenylethyl alcohol, which has a fruit-like aroma, was the most prevalent. In conclusion, the strains characterized here have relevant brewing properties and are exploitable as indigenous craft beer starters.
Keywords: Pichia membranifaciens; STA1 gene; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Saccharomyces uvarum; craft brewing; dextrin; hybrid; sour beer.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.B. was employed by Ca’ Del Brado Brewery. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Influence of indigenous Hanseniaspora uvarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae from sugar-rich substrates on the aromatic composition of loquat beer.Int J Food Microbiol. 2022 Oct 16;379:109868. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109868. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Int J Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35961159
-
Fermentative and metabolic screening of candidate yeast strains hybridisable with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for beer production optimisation.Int J Food Microbiol. 2025 Jan 2;426:110899. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110899. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Int J Food Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39244812
-
Hybridization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sourdough Strains with Cryotolerant Saccharomyces bayanus NBRC1948 as a Strategy to Increase Diversity of Strains Available for Lager Beer Fermentation.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 2;9(3):514. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030514. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33801403 Free PMC article.
-
[Non-conventional yeasts as tools for innovation and differentiation in brewing].Rev Argent Microbiol. 2021 Oct-Dec;53(4):359-377. doi: 10.1016/j.ram.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33674169 Review. Spanish.
-
A Review of N-Heterocycles: Mousy Off-Flavor in Sour Beer.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 10;72(14):7618-7628. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09776. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38538519 Review.
References
-
- Carbone A., Quici L. Craft beer mon amour: An exploration of Italian craft consumers. Br. Food J. 2020;122:2671–2687. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-07-2019-0476. - DOI
-
- Aquilani B., Laureti T., Poponi S., Secondi L. Beer choice and consumption determinants when craft beers are tasted: An exploratory study of consumer preferences. Food Qual. Pref. 2015;41:214–224. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2014.12.005. - DOI
-
- Viejo C.G., Fuentes S. Beer aroma and quality traits assessment using artificial intelligence. Fermentation. 2020;6:56. doi: 10.3390/fermentation6020056. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

