Guanylate-Binding Protein 2 Exerts GTPase-Dependent Anti-Ectromelia Virus Effect
- PMID: 37764102
- PMCID: PMC10534507
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11092258
Guanylate-Binding Protein 2 Exerts GTPase-Dependent Anti-Ectromelia Virus Effect
Abstract
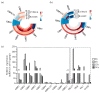
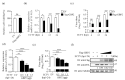
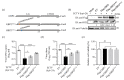
Guanylate-binding proteins (GBPs) are highly expressed interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) that play significant roles in protecting against invading pathogens. Although their functions in response to RNA viruses have been extensively investigated, there is limited information available regarding their role in DNA viruses, particularly poxviruses. Ectromelia virus (ECTV), a member of the orthopoxvirus genus, is a large double-stranded DNA virus closely related to the monkeypox virus and variola virus. It has been intensively studied as a highly effective model virus. According to the study, GBP2 overexpression suppresses ECTV replication in a dose-dependent manner, while GBP2 knockdown promotes ECTV infection. Additionally, it was discovered that GBP2 primarily functions through its N-terminal GTPase activity, and the inhibitory effect of GBP2 was disrupted in the GTP-binding-impaired mutant GBP2K51A. This study is the first to demonstrate the inhibitory effect of GBP2 on ECTV, and it offers insights into innovative antiviral strategies.
Keywords: GTPase; IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs); ectromelia virus (ECTV); guanylate binding protein (GBP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Viral Protein Poly(A) Polymerase Catalytic Subunit Interacts with Guanylate-Binding Proteins 2 to Antagonize the Antiviral Ability of Targeting Ectromelia Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 30;24(21):15750. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115750. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958732 Free PMC article.
-
Ectromelia virus upregulates the expression of heat shock protein 70 to promote viral replication.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Aug;42(2):1044-1053. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3655. Epub 2018 May 4. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29749430
-
Guanylate-Binding Protein 1, an Interferon-Induced GTPase, Exerts an Antiviral Activity against Classical Swine Fever Virus Depending on Its GTPase Activity.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4412-4426. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02718-15. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26889038 Free PMC article.
-
Ectromelia virus: the causative agent of mousepox.J Gen Virol. 2005 Oct;86(Pt 10):2645-2659. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81090-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 16186218 Review.
-
Regulation of innate immune functions by guanylate-binding proteins.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jan;308(1):237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29174633 Review.
Cited by
-
Guanylate-binding protein-5 is involved in inflammasome activation by bacterial DNA but only the cooperation of multiple GBPs accounts for control of Brucella abortus infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 8;15:1341464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1341464. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38404575 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle disease virus promotes pyroptosis in medulloblastoma cells by regulating interferon-gamma-mediated guanylate-binding protein 1 expression and activating caspase-4.Cytojournal. 2024 Oct 30;21:39. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_39_2024. eCollection 2024. Cytojournal. 2024. PMID: 39563668 Free PMC article.
-
The Viral Protein Poly(A) Polymerase Catalytic Subunit Interacts with Guanylate-Binding Proteins 2 to Antagonize the Antiviral Ability of Targeting Ectromelia Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 30;24(21):15750. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115750. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sigal L.J. The pathogenesis and immunobiology of mousepox. Adv. Immunol. 2016;129:251–276. - PubMed
-
- Xu R.H., Wong E.B., Rubio D., Roscoe F., Ma X., Nair S., Remakus S., Schwendener R., John S., Shlomchik M., et al. Sequential activation of two pathogen-sensing pathways is required for type I interferon expression and resistance to an acute DNA virus infection. Immunity. 2015;43:1148–1159. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

