Genomic Characterization of IMP-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Bulgaria Reveals the Emergence of IMP-100, a Novel Plasmid-Mediated Variant Coexisting with a Chromosomal VIM-4
- PMID: 37764114
- PMCID: PMC10537328
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11092270
Genomic Characterization of IMP-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Bulgaria Reveals the Emergence of IMP-100, a Novel Plasmid-Mediated Variant Coexisting with a Chromosomal VIM-4
Abstract
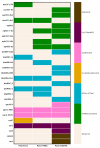
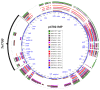
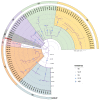
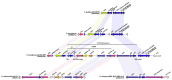
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections represent a major public health concern and require comprehensive understanding of their genetic makeup. This study investigated the first occurrence of imipenemase (IMP)-carrying P. aeruginosa strains from Bulgaria. Whole genome sequencing identified a novel plasmid-mediated IMP-100 allele located in a a novel In4886 integron embedded in a putative Tn7700 transposon. Two other closely related chromosomal IMP variants, IMP-13 and IMP-84, were also detected. The IMP-producers were resistant to last-line drugs including cefiderocol (CFDC) (two out of three) and susceptible to colistin. The IMP-13/84 cassettes were situated in a In320 integron inserted in a Tn5051-like transposon as previously reported. Lastly, the p4782-IMP plasmid rendered the PA01 transformant resistant to CFDC, suggesting a transferable CFDC resistance. A variety of virulence factors associated with adhesion, antiphagocytosis, iron uptake, and quorum sensing, as well as secretion systems, toxins, and proteases, were confirmed, suggesting significant pathogenic potential consistent with the observed strong biofilm formation. The emergence of IMP-producing MDR P. aeruginosa is alarming as it remains unsusceptible even to last-generation drugs like CFDC. Newly detected IMP-100 was even located in a CFDC-resistant XDR strain.
Keywords: Pseudomonas; blaIMP; metallo-beta-lactamase; novel allele; plasmid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cefiderocol: An Overview of Its in-vitro and in-vivo Activity and Underlying Resistant Mechanisms.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 7;8:741940. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.741940. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34950677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic characterization of a novel metallo-beta-lactamase gene, blaIMP-13, harboured by a novel Tn5051-type transposon disseminating carbapenemase genes in Europe: report from the SENTRY worldwide antimicrobial surveillance programme.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003 Oct;52(4):583-90. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg410. Epub 2003 Sep 1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12951335
-
Detection of VIM-2-, IMP-1- and NDM-1-producing multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Malaysia.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018 Jun;13:271-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2018.01.026. Epub 2018 Feb 9. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018. PMID: 29432937
-
An XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST463 Strain with an IncP-2 Plasmid Containing a Novel Transposon Tn6485f Encoding blaIMP-45 and blaAFM-1 and a Second Plasmid with Two Copies of blaKPC-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0446222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04462-22. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36651737 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Characteristics of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Chemother. 2015 Jun;47(2):81-97. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.81. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Infect Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26157586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Characterization of 16S rRNA Methyltransferase-Producing Enterobacterales Reveals the Emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST6260 Harboring rmtF, rmtB, blaNDM-5, blaOXA-232 and blaSFO-1 Genes in a Cancer Hospital in Bulgaria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;13(10):950. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100950. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452216 Free PMC article.
-
The fitness connection of antibiotic resistance.Front Microbiol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1556656. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1556656. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40276228 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Insights into Vietnamese Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-9-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates Belonging to the High-Risk Clone ST357 Obtained from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 25;13(9):719. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090719. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39338911 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacter hormaechei, Serratia marcescens, Citrobacter freundii, Providencia stuartii, and Morganella morganii Clinical Isolates from Bulgaria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 16;13(5):455. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050455. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zavascki A.P., Barth A.L., Gonçalves A.L.S., Moro A.L.D., Fernandes J.F., Martins A.F., Ramos F., Goldani L.Z. The influence of metallo- -lactamase production on mortality in nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006;58:387–392. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl239. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

