Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Comparative Pilot Study between Individuals Infected by SARS-CoV-2 during the Wild-Type and the Delta Periods
- PMID: 37764191
- PMCID: PMC10536989
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11092347
Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Comparative Pilot Study between Individuals Infected by SARS-CoV-2 during the Wild-Type and the Delta Periods
Abstract
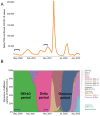
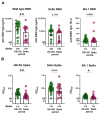
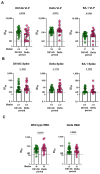
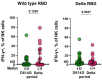
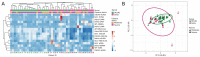
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, humanity has experienced the spread and circulation of several SARS-CoV-2 variants that differed in transmissibility, contagiousness, and the ability to escape from vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies. However, issues related to the differences in the variant-specific immune responses remain insufficiently studied. The aim of this study was to compare the parameters of the humoral immune responses in two groups of patients with acute COVID-19 who were infected during the circulation period of the D614G and the Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2. Sera from 48 patients with acute COVID-19 were tested for SARS-CoV-2 binding and neutralizing antibodies using six assays. We found that serum samples from the D614G period demonstrated 3.9- and 1.6-fold increases in RBD- and spike-specific IgG binding with wild-type antigens compared with Delta variant antigens (p < 0.01). Cluster analysis showed the existence of two well-separated clusters. The first cluster mainly consisted of D614G-period patients and the second cluster predominantly included patients from the Delta period. The results thus obtained indicate that humoral immune responses in D614G- and Delta-specific infections can be characterized by variant-specific signatures. This can be taken into account when developing new variant-specific vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; variants of concern; virus neutralization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khoury D.S., Cromer D., Reynaldi A., Schlub T.E., Wheatley A.K., Juno J.A., Subbarao K., Kent S.J., Triccas J.A., Davenport M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021;27:1205–1211. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01377-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ariën K.K., Heyndrickx L., Michiels J., Vereecken K., Van Lent K., Coppens S., Willems B., Pannus P., Martens G.A., Van Esbroeck M., et al. Three Doses of BNT162b2 Vaccine Confer Neutralising Antibody Capacity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. NPJ Vaccines. 2022;7:35. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00459-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker M., Cossmann A., Lürken K., Junker D., Gruber J., Juengling J., Ramos G.M., Beigel A., Wrenger E., Lonnemann G., et al. Longitudinal Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses after Triple BNT162b2 and Fourth Full-Dose MRNA-1273 Vaccination in Haemodialysis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:1004045. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1004045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goel R.R., Apostolidis S.A., Painter M.M., Mathew D., Pattekar A., Kuthuru O., Gouma S., Hicks P., Meng W., Rosenfeld A.M., et al. Distinct Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in SARS-CoV-2 Naïve and Recovered Individuals Following MRNA Vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021;6:eabi6950. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abi6950. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

