A Review of the Effect of Plasticizers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Alginate-Based Films
- PMID: 37764413
- PMCID: PMC10534897
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28186637
A Review of the Effect of Plasticizers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Alginate-Based Films
Abstract
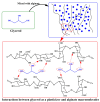
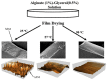
In recent years, there has been a growing attempt to manipulate various properties of biodegradable materials to use them as alternatives to their synthetic plastic counterparts. Alginate is a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed or soil bacteria that is considered one of the most promising materials for numerous applications. However, alginate potential for various applications is relatively limited due to brittleness, poor mechanical properties, scaling-up difficulties, and high water vapor permeability (WVP). Choosing an appropriate plasticizer can alleviate the situation by providing higher flexibility, workability, processability, and in some cases, higher hydrophobicity. This review paper discusses the main results and developments regarding the effects of various plasticizers on the properties of alginate-based films during the last decades. The plasticizers used for plasticizing alginate were classified into different categories, and their behavior under different concentrations and conditions was studied. Moreover, the drawback effects of plasticizers on the mechanical properties and WVP of the films are discussed. Finally, the role of plasticizers in the improved processing of alginate and the lack of knowledge on some aspects of plasticized alginate films is clarified, and accordingly, some recommendations for more classical studies of the plasticized alginate films in the future are offered.
Keywords: alginate; films; hydrophilic and hydrophobic plasticizers; physical and mechanical properties; plasticization mechanisms; water vapor permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdullah N.A., Mohamad Z., Khan Z.I., Jusoh M., Zakaria Z.Y., Ngadi N. Alginate Based Sustainable Films and Composites for Packaging: A Review. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021;83:271–276. doi: 10.3303/CET2183046. - DOI
-
- Gheorghita R., Gutt G., Amariei S. The Use of Edible Films Based on Sodium Alginate in Meat Product Packaging: An Eco-Friendly Alternative to Conventional Plastic Materials. Coatings. 2020;10:166. doi: 10.3390/coatings10020166. - DOI
-
- Castro-Yobal M.A., Contreras-Oliva A., Saucedo-Rivalcoba V., Rivera-Armenta J.L., Hernández-Ramírez G., Salinas-Ruiz J., Herrera-Corredor A. Evaluation of physicochemical properties of film-based alginate for food packing applications. e-Polymers. 2021;21:82–95. doi: 10.1515/epoly-2021-0011. - DOI
-
- Khairunnisa S., Junianto J., Zahidah Z., Rostini I. The effect of glycerol concentration as a plasticizer on edible films made from alginate towards its physical characteristic. World Sci. News. 2018;112:130–141.
-
- Galgano F., Condelli N., Favati F., Bianco D., Perretti G., Caruso M. Biodegradable packaging and EDIBLE COATING for fresh-cut fruits and vegetables. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2015;27:1–20. doi: 10.14674/1120-1770/ijfs.v70. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

